Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two angles of a quadrilateral are 89° and 113°. If the other two angles are equal; find the equal angles.
उत्तर
Let the other angle = x°
According to given,
89° + 113° + x° + x° = 360°
2x° = 360° – 202°
2x° = 158°
x° = `158/2`
other two angles = 79° each
संबंधित प्रश्न
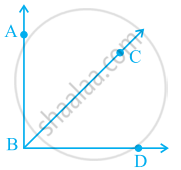
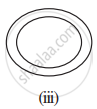
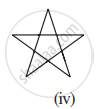
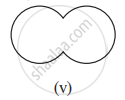
Given here are some figures:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Classify each of them on the basis of the following:
- Simple curve
- Simple closed curve
- Polygon
- Convex polygon
- Concave polygon
The perimeter of a parallelogram is 22 cm . If the longer side measures 6.5 cm what is the measure of the shorter side?
Define the following term Quadrilateral .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Sides.
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Diagonals .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Interior .
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has ..... vertices, no three of which are .....
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The sum of the angles of a quiadrilateral is .... right angles.
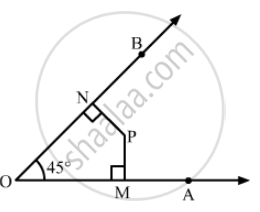
In Fig. 16.20, find the measure of ∠MPN.
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If in a quadrilateral only one pair of opposite sides are parallel, the quadrilateral is ................
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
A line drawn from the mid-point of one side of a triangle .............. another side intersects the third side at its mid-point.
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If both pairs of opposite sides of a quadrilateral are equal, then it is necessarily a ...............
The following figure shows a quadrilateral in which sides AB and DC are parallel. If ∠A : ∠D = 4 : 5, ∠B = (3x – 15)° and ∠C = (4x + 20)°, find each angle of the quadrilateral ABCD.
ABCDE is a regular pentagon. The bisector of angle A of the pentagon meets the side CD in point M. Show that ∠AMC = 90°.
The angles A, B, C and D of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 2 : 3 : 2 : 3. Show this quadrilateral is a parallelogram.
In a parallelogram ABCD, its diagonals AC and BD intersect each other at point O.
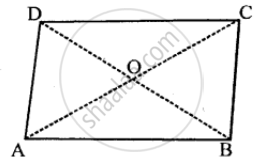
If AC = 12 cm and BD = 9 cm ; find; lengths of OA and OD.
In parallelogram ABCD, its diagonals intersect at point O. If OA = 6 cm and OB = 7.5 cm, find the length of AC and BD.

The angles of a hexagon are (2x + 5)°, (3x - 5)°, (x + 40)°, (2x + 20)°, (2x + 25)° and (2x + 35)°. Find the value of x.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, ∠A = 72° and ∠C is the supplementary of ∠A. The other two angles are 2x – 10 and x + 4. Find the value of x and the measure of all the angles
Three angles of a quadrilateral are 75º, 90º and 75º. The fourth angle is ______.
A diagonal of a rectangle is inclined to one side of the rectangle at 25º. The acute angle between the diagonals is ______.
D and E are the mid-points of the sides AB and AC respectively of ∆ABC. DE is produced to F. To prove that CF is equal and parallel to DA, we need an additional information which is ______.
What is the maximum number of obtuse angles that a quadrilateral can have?
In quadrilateral HOPE, the pairs of opposite sides are ______.
Both the pairs of opposite angles of a quadrilateral are equal and supplementary. Find the measure of each angle.
If a bicycle wheel has 48 spokes, then the angle between a pair of two consecutive spokes is ______.
In figure, ∠XYZ cannot be written as ______.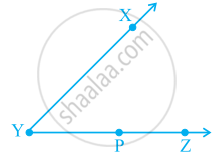
If the sum of two angles is equal to an obtuse angle, then which of the following is not possible?
In given figure, What is AC – EC?
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
BA ⊥BD