Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two angles of a quadrilateral are 89° and 113°. If the other two angles are equal; find the equal angles.
Solution
Let the other angle = x°
According to given,
89° + 113° + x° + x° = 360°
2x° = 360° – 202°
2x° = 158°
x° = `158/2`
other two angles = 79° each
RELATED QUESTIONS
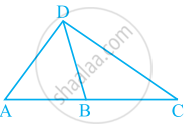
Given here are some figures:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Classify each of them on the basis of the following:
- Simple curve
- Simple closed curve
- Polygon
- Convex polygon
- Concave polygon
How many diagonals does following have?
A triangle
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Diagonals .
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has ....... sides.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has ...... angles.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has ..... vertices, no three of which are .....
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has .... diagonals.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The number of pairs of opposite angles of a quadrilateral is .......
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The measure of each angle of a convex quadrilateral is ..... 180°.
Two angles of a quadrilateral are of measure 65° and the other two angles are equal. What is the measure of each of these two angles?
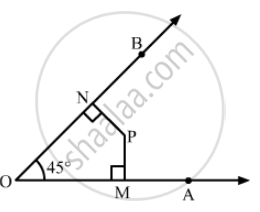
In Fig. 16.20, find the measure of ∠MPN.
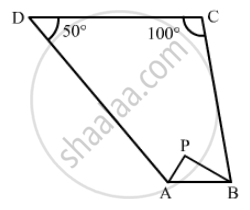
In Fig. 16.21, the bisectors of ∠A and ∠B meet at a point P. If ∠C = 100° and ∠D = 50°, find the measure of ∠APB.
In a convex hexagon, prove that the sum of all interior angle is equal to twice the sum of its exterior angles formed by producing the sides in the same order.
PQRSTU is a regular hexagon. Determine each angle of ΔPQT.
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If both pairs of opposite sides of a quadrilateral are equal, then it is necessarily a ...............
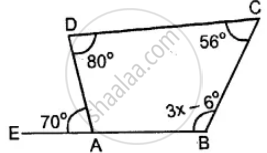
Use the information given in the following figure to find the value of x.
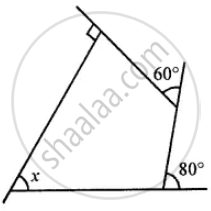
Use the following figure to find the value of x
The angles of a hexagon are (2x + 5)°, (3x - 5)°, (x + 40)°, (2x + 20)°, (2x + 25)° and (2x + 35)°. Find the value of x.
Calculate the measure of each angle of a nonagon.
The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 2 : 4 : 5 : 7. Find all the angles
A diagonal of a rectangle is inclined to one side of the rectangle at 25º. The acute angle between the diagonals is ______.
Measures of the two angles between hour and minute hands of a clock at 9 O’ clock are ______.
If a bicycle wheel has 48 spokes, then the angle between a pair of two consecutive spokes is ______.
In given figure, name any two angles that appear to be obtuse angles.
In given figure, What is BD – BE?
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
AC ⊥ BD
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
RS ⊥ RW
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
AE ⊥ CE
What conclusion can be drawn from part of given figure, if DB is the bisector of ∠ADC?