Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two angles of a quadrilateral are 68° and 76°. If the other two angles are in the ratio 5 : 7; find the measure of each of them.
Solution
Two angles are 68° and 76°
Let other two angles be 5x and 7x
68° + 76°+ 5x + 7x = 360°
12x + 144° = 360°
12x = 360° – 144°
12x = 216°
x = 18°
angles are 5x and 7x
i.e. 5 x 18° and 7 x 18° i.e. 90° and 126°
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How many diagonals does following have?
A triangle
Define the following term Quadrilateral .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Sides.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A diagonal of a quadrilateral is a line segment that joins two ...... vertices of the quadrilateral.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A point is in the interior of a convex quadrilateral, if it is in the ..... of its two opposite angles.
The sides of a quadrilateral are produced in order. What is the sum of the four exterior angles?
The measure of angles of a hexagon are x°, (x − 5)°, (x − 5)°, (2x − 5)°, (2x − 5)°, (2x + 20)°. Find the value of x.
Determine the number of sides of a polygon whose exterior and interior angles are in the ratio 1 : 5.
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
A line drawn from the mid-point of one side of a triangle .............. another side intersects the third side at its mid-point.
Three angles of a quadrilateral are equal. If the fourth angle is 69°; find the measure of equal angles.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, AO and BO are bisectors of angle A and angle B respectively. Show that:
∠AOB = (∠C + ∠D)
In a trapezium ABCD, side AB is parallel to side DC. If ∠A = 78° and ∠C = 120. find angles B and D.
Two diagonals of an isosceles trapezium are x cm and (3x – 8) cm. Find the value of x.
Angle A of an isosceles trapezium ABCD is 115°; find the angles B, C and D.
If three angles of a quadrilateral are 90° each, show that the given quadrilateral is a rectangle.
Observe the figure below and find out their name.
The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 2 : 4 : 5 : 7. Find all the angles
If bisectors of ∠A and ∠B of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect each other at P, of ∠B and ∠C at Q, of ∠C and ∠D at R and of ∠D and ∠A at S, then PQRS is a ______.
Which of the following is not true for a parallelogram?
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AB || DC and AD = BC. Prove that ∠A = ∠B and ∠C = ∠D.
In quadrilateral WXYZ, the pairs of opposite angles are ______.
Number of angles less than 180° in figure is ______ and their names are ______.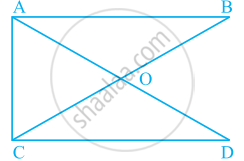
In given figure, name any four angles that appear to be acute angles.
In given figure, What is AE + EC?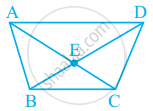
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
AC ⊥ BD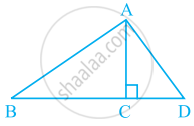
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
OP ⊥ AB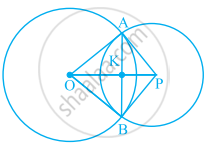
An angle is said to be trisected, if it is divided into three equal parts. If in the given figure, ∠BAC = ∠CAD = ∠DAE, how many trisectors are there for ∠BAE?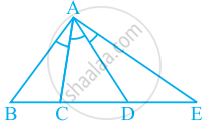
Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral PQRS. Draw its diagonals. Name them. Is the meeting point of the diagonals in the interior or exterior of the quadrilateral?