Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two angles of a quadrilateral are 68° and 76°. If the other two angles are in the ratio 5 : 7; find the measure of each of them.
उत्तर
Two angles are 68° and 76°
Let other two angles be 5x and 7x
68° + 76°+ 5x + 7x = 360°
12x + 144° = 360°
12x = 360° – 144°
12x = 216°
x = 18°
angles are 5x and 7x
i.e. 5 x 18° and 7 x 18° i.e. 90° and 126°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How many diagonals does following have?
A regular hexagon
How many diagonals does following have?
A triangle
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The sum of the angles of a quiadrilateral is .... right angles.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral is convex if, for each side, the remaining ______ lie on the same side of the line containing the side.
The four angles of a quadrilateral are as 3 : 5 : 7 : 9. Find the angles.
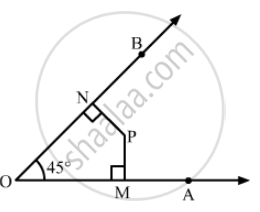
In Fig. 16.20, find the measure of ∠MPN.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, CO and DO are the bisectors of ∠C and ∠D respectively. Prove that \[∠COD = \frac{1}{2}(∠A + ∠B) .\]
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is three times the sum of its exterior angles. Determine the number of sided of the polygon.
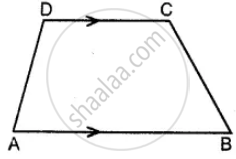
In the given figure, ABCD is a trapezium. Find the values of x and y.

Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
f consecutive sides of a parallelogram are equal, then it is necessarily a ..................
The consecutive sides of a quadrilateral have
In quadrilateral ABCD, side AB is parallel to side DC. If ∠A : ∠D = 1 : 2 and ∠C : ∠B = 4 : 5
(i) Calculate each angle of the quadrilateral.
(ii) Assign a special name to quadrilateral ABCD
The following figure shows a quadrilateral in which sides AB and DC are parallel. If ∠A : ∠D = 4 : 5, ∠B = (3x – 15)° and ∠C = (4x + 20)°, find each angle of the quadrilateral ABCD.
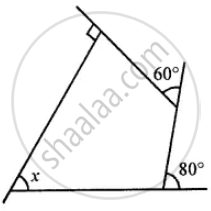
Use the following figure to find the value of x
In a parallelogram ABCD, its diagonals AC and BD intersect each other at point O.
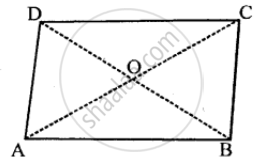
If AC = 12 cm and BD = 9 cm ; find; lengths of OA and OD.
Write, giving reason, the name of the figure drawn alongside. Under what condition will this figure be a square.
Observe the figure below and find out their name.
The angles of a hexagon are (2x + 5)°, (3x - 5)°, (x + 40)°, (2x + 20)°, (2x + 25)° and (2x + 35)°. Find the value of x.
The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 2 : 4 : 5 : 7. Find all the angles
If one angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is 75°, then the opposite angle is
In quadrilateral WXYZ, the pairs of opposite angles are ______.
In figure, if point A is shifted to point B along the ray PX such that PB = 2PA, then the measure of ∠BPY is ______.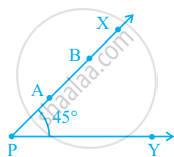
The number of obtuse angles in figure is ______.
In the given figure.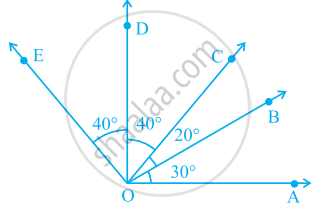
∠AOD is a/an ____ angle
The common part between the two angles BAC and DAB in figure is ______.
What conclusion can be drawn from part of given figure, if BD bisects ∠ABC?
Can we have two obtuse angles whose sum is a complete angle? Why or why not?
Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral KLMN. State two pairs of opposite angles.
Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral KLMN. State two pairs of adjacent angles.
