Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If both pairs of opposite sides of a quadrilateral are equal, then it is necessarily a ...............
Options
rectangle
parallelogram
rhombus
Solution
If both pairs of opposite sides of a quadrilateral are equal, then it is necessarily a parallelogram.
Reason:
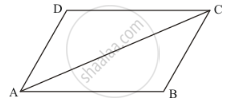
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AB = CD and BC = DA.
We need to show that ABCD is a parallelogram.
In Δ ACB and ΔCAD, we have
AC = CA (Common)
CB = AD (Given)
AB = CD (Given)
So, by SSS criterion of congruence, we have
ΔACB ≅ ΔCAD
By corresponding parts of congruent triangles property.
∠CAB =∠ACD …… (i)
And ∠ACB = ∠CAD
Now lines AC intersects AB and DC at A and C,such that
∠CAB = ∠ACD (From (i))
That is, alternate interior angles are equal.
Therefore, . AB || DC
Similarly, AD || BC
Therefore, ABCD is a parallelogram.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Diagonals .
The three angles of a quadrilateral are respectively equal to 110°, 50° and 40°. Find its fourth angle.
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If in a quadrilateral only one pair of opposite sides are parallel, the quadrilateral is ................
Two angles of a quadrilateral are 68° and 76°. If the other two angles are in the ratio 5 : 7; find the measure of each of them.
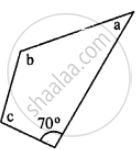
In the given figure : ∠b = 2a + 15 and ∠c = 3a + 5; find the values of b and c.
Find the angles of a pentagon which are in the ratio 4: 4: 6: 7: 6.
In the quadrilateral ABCD, AB = BC and AD = DC Measure of ∠BCD is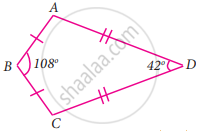
In figure, ∠XYZ cannot be written as ______.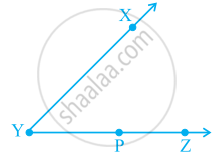
In the given figure.
∠AOE is a/an ______ angle
Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral KLMN. State two pairs of opposite angles.
