Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If opposite angles of a quadrilateral are equal, then it is necessarily a ....................
Options
parallelogram
rhombus
rectangle
Solution
If opposite angles of a quadrilateral are equal, then it is necessarily a parallelogram.
Reason:

ABCD is a quadrilateral in which ∠A =∠C and ∠B = ∠D.
We need to show that ABCD is a parallelogram.
In quadrilateral ABCD, we have
∠A = ∠C
∠B = ∠D
Therefore,
∠A + ∠B = ∠C + ∠D …… (i)
Since sum of angles of a quadrilateral is 360°
∠A + ∠B = ∠C + ∠D = 360°
From equation (i), we get:
(∠A + ∠B) + ( ∠A + ∠B) = 360°
2(∠A +∠B ) = 360°
∠A + ∠B = 180°
Similarly, ∠C + ∠D = 180°
Now, line AB intersects AD and BC at A and B respectively
Such that ∠A +∠B = 180°
That is, sum of consecutive interior angles is supplementary.
Therefore, .AD || BC
Similarly, we get AB || DC.
Therefore, ABCD is a parallelogram.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How many diagonals does following have?
A triangle
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
In a quadrilateral the point of intersection of the diagonals lies in .... of the quadrilateral.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral is convex if, for each side, the remaining ______ lie on the same side of the line containing the side.
In Fig. 16.19, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
How many pairs of adjacent sides are there?
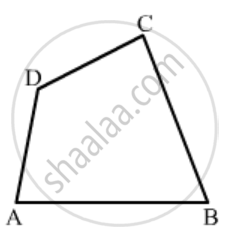
In Fig. 16.19, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
Name a pair of adjacent angles.
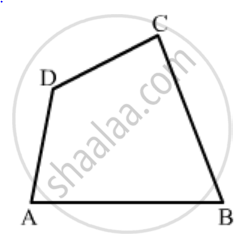
In parallelogram ABCD, its diagonals intersect at point O. If OA = 6 cm and OB = 7.5 cm, find the length of AC and BD.

ABCD is a rhombus such that ∠ACB = 40º. Then ∠ADB is ______.
In figure, ∠XYZ cannot be written as ______.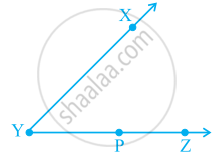
What conclusion can be drawn from part of given figure, if DB is the bisector of ∠ADC?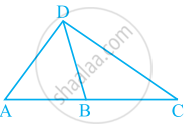
Can we have two obtuse angles whose sum is an acute angle? Why or why not?
