Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Both the pairs of opposite angles of a quadrilateral are equal and supplementary. Find the measure of each angle.
उत्तर
Let ABCD be a quadrilateral.
So, ∠A = ∠C
∠B = ∠D
And ∠A + ∠C = 180°, ∠B + ∠D = 180°
Now, ∠A + ∠A = 180° ...[∠C = ∠A]
⇒ 2∠A = 180°
⇒ ∠A = 90°
Similarly, ∠B = 90°
Hence, each angle is a right angle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Sides.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has ..... vertices, no three of which are .....
If ABCD is a rectangle with ∠BAC = 32°, find the measure of ∠DBC.
Which of the following quadrilateral is not a rhombus?
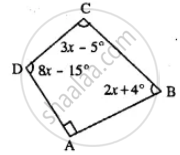
Use the information given in the following figure to find :
(i) x
(ii) ∠B and ∠C
The angles of a pentagon are x°, (x - 10)°, (x + 20)°, (2x - 44)° and (2x - 70)°. Find the angles.
ΔPQR and ΔSQR are on the same base QR with P and S on opposite sides of line QR, such that area of ΔPQR is equal to the area of ΔSQR. Show that QR bisects PS.
In the quadrilateral ABCD, AB = BC and AD = DC Measure of ∠BCD is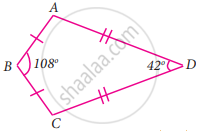
The common part between the two angles BAC and DAB in figure is ______.
Draw a rough sketch of a quadrilateral KLMN. State two pairs of adjacent angles.
