Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
ΔPQR and ΔSQR are on the same base QR with P and S on opposite sides of line QR, such that area of ΔPQR is equal to the area of ΔSQR. Show that QR bisects PS.
उत्तर
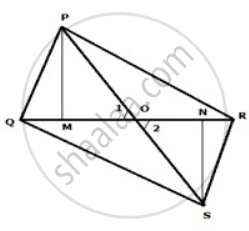
Join PS. Suppose PS and QR intersect at O. Draw PM and SN perpendicular to QR.
ar(ΔPQR) = ar(ΔSQR)
Thus ΔPQR and ΔSQR are on the same base QR and have equal area.
Therefore, their corresponding altitudes are equal i.e. PM = SN.
Now,
In ΔPMO and ΔSNO.
∠1 = ∠2 ...(vertically opposite angles)
∠PMO = ∠SNO ...(right angles)
PM = SN
Therefore, ΔPMO ≅ ΔSNO ..(AAS axiom)
⇒ PO = OS
⇒ QR bisects PS.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If in a quadrilateral only one pair of opposite sides are parallel, the quadrilateral is ................
Angles of a quadrilateral are (4x)°, 5(x+2)°, (7x – 20)° and 6(x+3)°. Find :
(i) the value of x.
(ii) each angle of the quadrilateral.
The following figure shows a quadrilateral in which sides AB and DC are parallel. If ∠A : ∠D = 4 : 5, ∠B = (3x – 15)° and ∠C = (4x + 20)°, find each angle of the quadrilateral ABCD.
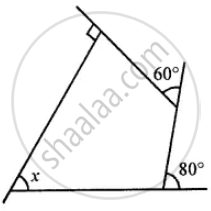
Use the following figure to find the value of x
In a pentagon ABCDE, AB || ED and ∠B = 140°, ∠C = 2x° and ∠D = 3x°. Find ∠C and ∠D
A diagonal of a rectangle is inclined to one side of the rectangle at 25º. The acute angle between the diagonals is ______.
In figure, if point A is shifted to point B along the ray PX such that PB = 2PA, then the measure of ∠BPY is ______.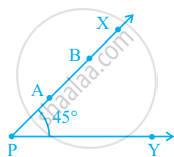
In given figure, name any four angles that appear to be acute angles.
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
RT ⊥ ST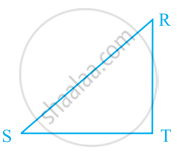
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
AC ⊥ BD