Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two tungsten bulbs of power 50 W and 60 W work on 220 V potential difference. If they are connected in parallel, how much current will flow in the main conductor?
उत्तर
Given: P1 = 50 W, P2 = 60 W and V = 220 V
To find I = ?
Formula: P = VI
We know,
Total Power (P) = P1 + P2
= 50 + 60
= 110 W
We know, P = VI
⇒ I = `"P"/"V"`
= `110/220`
= `1/2`
I = 0.5 A
The current of 0.5 A will flow in the main conductor.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Redraw the circuit of question 1, putting in an ammeter to measure the current through the resistors and a voltmeter to measure the potential difference across the 12 Ω resistors. What would be the readings in the ammeter and the voltmeter?
Draw circuit symbols for
fixed resistance
Draw circuit symbols for
a cell
Tell the odd one out. Give proper explanation.
Who will spend more electrical energy? 500 W TV Set in 30 mins, or 600 W heater in 20 mins?
Find the odd one out and justify it.
Fuse wire, M.C.B., Rubber Gloves, Generator
In an electric circuit, electron flow a from of point of ______ potential to the point of ______ potential.
Write the condition required for a circuit to be a closed circuit.
What do you understand by the open electric circuit?
Explain the following:
Open circuit
Explain the following:
Closed circuit
What is open circuit?
In any electric circuit, when the switch is on and the current flows through it why do the wire, switches, bulb or devices become hot?
The unit of electrical power is _______.
What is the use of earthing wire?
Draw the circuit diagram for the series connection.
In the circuit diagram below, 10 units of electric charge move past point x every second What is the current in the circuit ______.
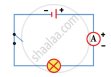
In the circuit shown, which switches (L,M or N) must be closed to light up the bulb?
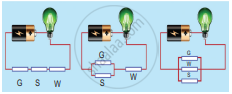
In which of the following circuits are the bulb connected in series?
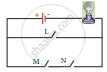
Study the three electric circuits below. Each of them has a glass rod (G), a steel rod (S), and a wooden rod (W).
In which of the electric circuits would the bulb not light up.
_____ has a thin metallic filament that melts and breaks the connection when the circuit is overheated.
Three bulbs are connected end to end from the battery. This connection is called _______.
When a circuit is open, _____ cannot pass through it.
What is the role of the earth wire in domestic circuits?
Explain about domestic electric circuits. (circuit diagram not required)
The rate of flow of electric charges in a circuit is called ______.
______ is a kind of fish which is able to produce an electric current.
In an electrical circuit three incandescent bulbs A, B and C of rating 40 W, 60 W and 100 W respectively are connected in parallel to an electric source. Which of the following is likely to happen regarding their brightness?
Draw a circuit diagram of an electric circuit containing a cell, a key, an ammeter, a resistor of 2Ω in series with a combination of two resistors (4Ω each) in parallel and a voltmeter across the parallel combination. Will the potential difference across the 2Ω resistor be the same as that across the parallel combination of 4Ω resistors? Give reason.
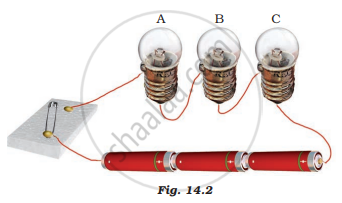
Three bulbs A, B, and C are connected in a circuit as shown in Figure 14.2. When the switch is ‘ON’
Draw the symbols of the following circuit components.
switch in off position
What are the essential components of an electric circuit?
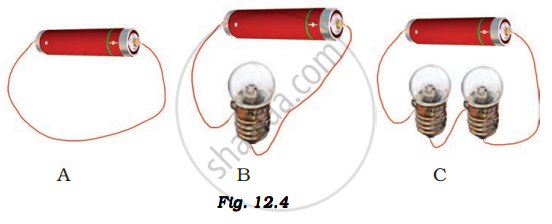
In which of the following circuits A, B, and C gave in Fig. 12.4, the cell will be used up very rapidly?
Name the device which is used to measure the strength of the electric current in an electric circuit.
An electric motor rated 1100 W is connected to 220 V mains. Find:
- The current drawn from the mains,
- Electric energy consumed if the motor is used for 5 hours daily for 6 days.
- Total cost of energy consumed if the rate of one unit is 5.
Set up the circuit shown in Figure again. Move the key to ‘ON’ position and watch carefully in which direction the compass needle gets deflected. Switch ‘OFF’ the current. Now keeping rest of the circuit intact, reverse the connections at the terminal of the cell. Again switch ‘on’ the current. Note the direction in which the needle gets deflected. Think of an explanation.