Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Use Gauss' law to derive the expression for the electric field `(vecE)` due to a straight uniformly charged infinite line of charge density λ C/m.
Use Gauss' law to obtain an expression for the electric field due to an infinitely long thin straight wire with uniform linear charge density λ.
उत्तर
Field due to an infinitely long straight uniformly charged wire,

Consider a thin, infinitely long straight line charge of linear charge density λ.
Let P be the point at a distance a from the line. To find the electric field at point P, draw a cylindrical surface of radius ‘a’ and length l.
If E is the magnitude of the electric field at point P, then electric flux through the Gaussian surface,
Φ = E × Area of the curved surface of a cylinder of radius r and length l
As electric lines of force are parallel to the end faces (circular caps) of the cylinder, there is no component of the field along the normal to the end faces.
Φ = E × 2πal …(i)
According to Gauss's Theorem,
`phi = q/epsilon_0`
`∵ q = lambdal`
`:. phi = (lambdal)/epsilon_0` ...(ii)
From equations (i) and (ii), we get:
`E xx 2pial = (lambdal)/epsilon_0`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why, for a charge configuration, the equipotential surface through a point is normal to the electric field at that point
"For any charge configuration, equipotential surface through a point is normal to the electric field." Justify.
Obtain the formula for the electric field due to a long thin wire of uniform linear charge density λ without using Gauss’s law. [Hint: Use Coulomb’s law directly and evaluate the necessary integral.]
A point charge q is at a distance of d/2 directly above the centre of a square of side d, as shown the figure. Use Gauss' law to obtain the expression for the electric flux through the square.
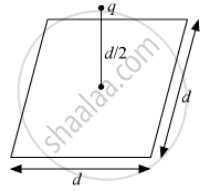
If the point charge is now moved to a distance 'd' from the centre of the square and the side of the square is doubled, explain how the electric flux will be affected.
Draw a graph to show the variation of E with perpendicular distance r from the line of charge.
Find the work done in bringing a charge q from perpendicular distance r1 to r2 (r2 > r1)
If the ratio of radii of two wires of same material is 3 : 1 and ratio of their lengths is 5 : 1, then the ratio of the normal forces that will produce the same extension in the length of two wires is:
A solid metal sphere of radius R having charge q is enclosed inside the concentric spherical shell of inner radius a and outer radius b as shown in the figure. The approximate variation of the electric field `vecE` as a function of distance r from centre O is given by ______.

An infinitely long positively charged straight wire has a linear charge density λ. An electron is revolving in a circle with a constant speed v such that the wire passes through the centre, and is perpendicular to the plane, of the circle. Find the kinetic energy of the electron in terms of the magnitudes of its charge and linear charge density λ on the wire.
