Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Use ruler and compasses only for the following questions. All constructions lines and arcs must be clearly shown
Mark 2 points X and Y which are a distance of 3.5 cm from A and also equidistant from AC and BC. Measure XY.
उत्तर
Steps for construction :
1) We known that the points at a distance of 3.5 cm from A will surely lie on the circle with centre A.
2) Also, the points on the angle bisector CH are the points equidistant from AC and BC.
3) Mark X and Y which are at the intersection of the circle and the angle bisector CH.
4) Measure XY. XY = 5 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use ruler and compasses only for the following questions. All constructions lines and arcs must be clearly shown.
Construct the locus of points at a distance of 3.5 cm from A.
A point moves such that its distance from a fixed line AB is always the same. What is the relation between AB and the path travelled by the point?
State the locus of a point moving so that its perpendicular distances from two given lines is always equal.
AB is a fixed line) state the locus of the point P such that ∠ APB = 90° .
The bisector of ∠ B and ∠C of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect in P, show that P is equidistant from the opposite sides AB and CD.
In ΔABC, the bisector AX of ∠A intersects BC ar X. XL ⊥ AB and XM ⊥ AC are drawn (Fig.) is XL = XM? why or why not?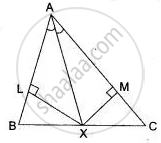
l is the perpendicular bisector of line segment PQ and R is a point on the same side of l as P. The segment QR intersects l at X. Prove that PX + XR = QR.
Given a Δ ABC with unequal sides. Find a point which is equidistant from B and C as well as from AB and AC.
The diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angles. Show that the quadrilateral is a rhombus.
What is the locus of points which are equidistant from the given non-collinear point A, B and C? Justify your answer.
