Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment value in the following:
\[\ce{[CoF6]^{3-}, [Co(H2O)6]^{2+}, [Co(Cn)6]^{3-}}\]
उत्तर
(1) \[\ce{[CoF6]^{3-}}\]:
\[\ce{Co^{3+} = 3d^6}\]
Number of unpaired electrons = 4
Magnetic moment = `sqrt(n(n + 2)) = sqrt(4(4 + 2))` = 4.9 BM
(ii) \[\ce{[Co(H2O)6]^{2+}}\]:

\[\ce{Co^{2+} = 3d^7}\]
Number of unpaired electrons = 3
Magnetic moment = `sqrt(3(3 + 2))` = 3.87 BM
(iii) \[\ce{[Co(CN)6]^{3-}}\]:
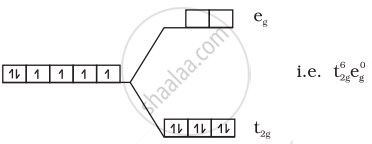
\[\ce{Co^{3+} = 3d^6}\]
No unpaired electrons so diamagnetic.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the superiority of crystal field theory over valence bond theory.
Draw the structures of the following :
(1) XeF6
(2) IF7
Why are low spin tetrahedral complexes not formed?
Arrange following complex ions in increasing order of crystal field splitting energy (∆O):
\[\ce{[Cr(Cl)6]^{3-}, [Cr(CN)6]^{3-}, [Cr(NH3)6]^{3+}}\].
\[\ce{CuSO4 . 5H2O}\] is blue in colour while \[\ce{CuSO4}\] is colourless. Why?
Why are different colours observed in octahedral and tetrahedral complexes for the same metal and same ligands?
[Ni(H2O)6]2+ (aq) is green in colour whereas [Ni(H2O)4 (en)]2+ (aq)is blue in colour, give reason in support of your answer.
The correct order of increasing crystal field strength in following series:
The CFSE of [CoCl6]3– is 18000 cm–1 the CFSE for [CoCl4]– will be ______.
On the basis of Crystal Field Theory, write the electronic configuration of d4 ion if Δ0 > P.
