Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the adverse effects of corrosion?
उत्तर
The adverse effects of corrosion are as follows:
- Damage to commercial aeroplanes that could result in possible in-flight problems
- Damage to oil pipelines that could cause a costly and dangerous rupture that creates significant environmental damage.
- Damage to bridge supports that could cause a bridge failure
- Release of harmful pollutants from iron corrosion that contaminates the air
- Costs of repairing or replacing household equipment that fails
- Lose of efficiency
- Contamination of product
- Damage of metallic equipments
- Inability to use metallic materials
- Lose of valuable materials such as blockage of pipes, mechanical damage of underground water pipes
- Accidents due to mechanical lose of metallic cars, aircrafts etc.
- Causes pollution due to escaping products from corrosion
- Depletion of natural resource
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which metals do not corrode easily?
The chemical reaction involved in the corrosion of iron metal is that of:
(a) oxidation as well as displacement
(b) reduction as well as combination
(c) oxidation as well as combination
(d) reduction as well as displacement
What is meant by 'rusting of iron'? With the help of labelled diagrams, describe an activity to find out the conditions under which iron rusts.
Explain why, when a copper object remains in damp air for a considerable time, a green coating is formed on its surface. What is this process known as?
Explain why, the galvanised iron article is protected against rusting even if the zinc layer is broken.
No chemical reaction takes place when granules of a rusty-brown solid A are mixed with the powder of another solid B. However, when the mixture is heated, a reaction takes place between its components. One of the products C is a metal and settles down in the molten state while the other product D floats over it. It was observed that the reaction is highly exothermic.
(a) What could the solids A and B be?
(b) What are the products C and D most likely to be?
(c) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between A and B leading to the formation of C and D. Mention the physical states of all the reactants and products in this equation and indicate the heat change which takes place.
(d) What is the special name of such a reaction? State one use of such a reaction.
(e) Name any two types of chemical reactions under which the above reaction can be classified.
Observe the following picture a write down the chemical reaction with the explanation.

Identify the process shown in the diagram and explain it in short
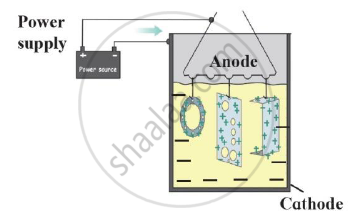
State two conditions necessary for rusting of iron.
Galvanisation is a method of protecting iron from rusting by coating it with a thin layer of ____________.
