Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in various organisms?
उत्तर १
At first glucose (6 carbon molecules) is broken in the cytoplasm of cells of all organisms. This process yields a 3 carbon molecule compound called pyruvate. Further break down of pyruvate takes place in different manners in different organisms.
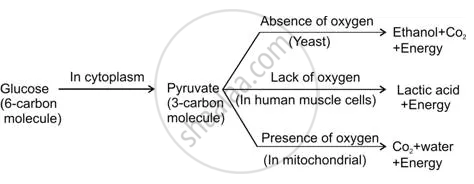
- Anaerobic Respiration: This process takes place in absence of oxygen, e.g. in yeast during fermentation. In this case pyruvate is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide.
- Aerobic Respiration: In aerobic respiration, breakdown of pyruvate takes place in presence of oxygen to give rise 3 molecules of carbon dioxide and water. The release of energy in aerobic respiration is much more than anaerobic respiration.
- Lack of Oxygen: Sometimes, when there is lack of oxygen, especially during vigorous activity, in our muscles, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid (3 carbon molecule compounds). Formation of lactic acid in muscles causes cramp.
उत्तर २
Glucose is oxidised in two ways to provide energy.
- Aerobic respiration: Glucose is completely oxidised to carbon dioxide and water in the presence of oxygen, with the release of a considerable amount of energy. This type of oxidation occurs in most of the living organisms such as human beings, birds, snakes, frogs, fish, etc.
- Anaerobic respiration: This type of respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen. In this type of oxidation, glucose is partially oxidised to ethanol and carbon dioxide (yeast and other bacteria) or lactic acid (muscles during physical exercise and some bacteria) with the release of a small amount of energy.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How are the lungs designed in human beings to maximize the area for exchange of gases?
How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
What would be the consequences of a deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
Trace the movement of oxygenated blood in the body.
The exchange of respiratory gases in the cells of plants occurs by the process of _______________
(a) Osmosis
(b) Diffusion
(c) Glycolysis
(d) exhalation
If a plant is releasing carbon dioxide and taking in oxygen during the day, does it mean that there is no photosynthesis occurring? Justify your answer.
Name the process by which plant parts like roots, stems, and leaves get oxygen required for respiration.
Name the areas in a woody stem through which respiratory exchange of gases takes place.
What is the name of tiny air-sacs at the end of smallest bronchioles in the lungs?
State whether the following statement is true or false:
Energy can be produced in cells without oxygen.
Explain why, a land plant may die if its roots remain waterlogged for a long time.
Define breathing. State the differences between breathing and respiration.
Describe the process of respiration in Amoeba. State whether it is anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration.
Describe the process of respiration in the following part of a plant:
Stem
Explain how, the air we breathe in gets cleaned while passing through the nasal passage.
Which contains more carbon dixoide : exhaled air or inhaled air? Why?
Which of the following is correct for the process of anaerobic respiration?
| Carbon dioxide always produced | A lot of energy released | |
| (a) | No | Yes |
| (b) | No | No |
| (c) | Yes | No |
| (d) | Yes | Yes |
Which of the following is the correct sequence of air passage during inhalation?
(a) nostrils → larynx → pharynx → trachea → lungs
(b) nasal passage → trachea → pharynx → larynx → alveoli
(c) larynx → nostrils → pharynx → lungs
(d) nostrils → pharynx → larynx → trachea → alevoli
During the deficiency of oxygen in tissues of human beings, pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid in:
The photosynthesis in a plant is not taking place during the day time if the plant is releasing:
One of the following organisms does not depend on the simple diffusion of gases for breathing and respiration. This organism is:
A, B and C are three living organisms. The organism A is a unicellullar fungus which can live without air. It is used in the commercial production of an organic compound P from molasses. The organism B is a unicellular animal which lives in water and feeds and moves by using pseudopodia. It breathes through an organelle Q. The organism C is a tiny animal which acts as a carrier of malarial parasite. It breathes and respires through a kind of tiny holes R and air-tubes S in its body.
(a) What are organisms (i) A (ii) B, and (iii) C?
(b) Name (i) P (ii) Q (iii) R, and (iv) S.
(c) Which organism/organisms undergo aerobic respiration?
(d) Which organism/organisms undergo anaerobic respiration?
There are five animals P, Q, R, S and T. The animal P always lives in water and has gills for breathing. The animal Q can stay in water as well as on land and can breathe both, through moist skin and lungs. The animal R lives in soil and breathes only through its skin. The animal S lives on land and breathes through spiracles and tracheae. And animal T lives in water and breathes through its cell membrane.
(a) Which of the animals could be Amoeba?
(b) Which of the animals could be frog?
(c) Which animal could be fish?
(d) Which animal could be grasshopper?
(e) Which animal could be earthworm?
Consider the following chemical reactions which take place in different organisms/tissues under various conditions:
(i) Glucose → Respiration ">Ethanol + Carbon dioxide + Energy
(ii) Glucose→ Respiration ">Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
(iii) Glucose → Respiration "> Lactic acid + Energy
(a) Name one organism which respires according to equation (i) above.
(b) Name one organism which respires according to equation (ii) above.
(c) When and where does respiration represented by equation (iii) above take place?
(d) Which equation/equations represent aerobic respiration?
(e) Which equation/equations represent anaerobic respiration?
(f) Which of the above reactions produces the maximum amount of energy?
Differentiate between
External respiration and Internal respiration
A student has set up "CO2 is released during respiration”. After about 1 hour he observes no change in the water level in the delivery tube. Write two possible resons for the failure of the experiment.
Name the body structure concerned with the given functional activity:
Provides actual diffusion of respiratory gases in the lungs.
Match the items in Column I with the ones most appropriate in Column II. Rewrite the matching pairs.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(a) Alveoli |
(i) where aerobic respiration takes place |
|
(b) Bronchioles |
(ii) lined with hair |
|
(c) Nasal Chamber |
(iii) diffusion of gases |
|
(d) Bronchi |
(iv) small air tubes |
|
(v) an inverted Y shaped tube |
|
|
(vi) a common passage for food and air |
Given below is an example of certain structure and its special functional activity:
"Kidney and excretion".
Fill in the blanks on a similar pattern.
Alveoli and _____________.
Given below is an example of certain structure and its special functional activity:
"Kidney and excretion".
Fill in the blanks on a similar pattern.
Diaphragm and _____________.
Given below is an example of certain structure and its special functional activity:
"Kidney and excretion".
Fill in the blanks on a similar pattern.
'C' shaped cartilage rings and ____________.
State one function of the following:
Mitochondria
What is the ppCO2 in alveolar air?
Sometimes we get painful cramps in our leg muscles after running for a long time due to the accumulation of:
Which is the correct sequence of air passage during inhalation?
During respiration exchange of gases take place in
Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
Match the correct answers with the type of respiration and respiratory substances.
| Respiration | Types of Substrates |
| A. Floating respiration | I. Proteins |
| B. Cytoplasmic respiration | II. Glucose |
| C. Protoplasmic respiration | III. Carbohydrates and fats |
