Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in various organisms?
Solution 1
At first glucose (6 carbon molecules) is broken in the cytoplasm of cells of all organisms. This process yields a 3 carbon molecule compound called pyruvate. Further break down of pyruvate takes place in different manners in different organisms.
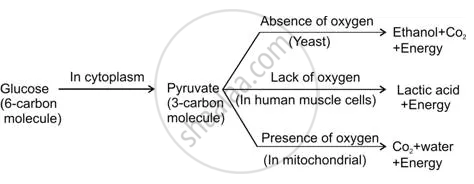
- Anaerobic Respiration: This process takes place in absence of oxygen, e.g. in yeast during fermentation. In this case pyruvate is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide.
- Aerobic Respiration: In aerobic respiration, breakdown of pyruvate takes place in presence of oxygen to give rise 3 molecules of carbon dioxide and water. The release of energy in aerobic respiration is much more than anaerobic respiration.
- Lack of Oxygen: Sometimes, when there is lack of oxygen, especially during vigorous activity, in our muscles, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid (3 carbon molecule compounds). Formation of lactic acid in muscles causes cramp.
Solution 2
Glucose is oxidised in two ways to provide energy.
- Aerobic respiration: Glucose is completely oxidised to carbon dioxide and water in the presence of oxygen, with the release of a considerable amount of energy. This type of oxidation occurs in most of the living organisms such as human beings, birds, snakes, frogs, fish, etc.
- Anaerobic respiration: This type of respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen. In this type of oxidation, glucose is partially oxidised to ethanol and carbon dioxide (yeast and other bacteria) or lactic acid (muscles during physical exercise and some bacteria) with the release of a small amount of energy.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? Name some organisms that use the anaerobic mode of respiration.
The trachea divides into tow tubes at its lower end. What is the name of these tubes?
What is the name of tiny air-sacs at the end of smallest bronchioles in the lungs?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Gills are the breathing organs in ___________.
Name the type of respiration in which the end product is:
Lactic acid
Give one example where such a respiration can occur.
Describe the process of respiration in the following part of a plant:
Leaves
Name the energy currency in the living organisms. When and where is it produced?
What are the major organs of respiratory system in man (or humans)?
How are oxygen and carbon dioxide exchanged in our body during respiration?
"Respiration is a vital function of the body". Justify this statements.
Which of the following increases in muscle cells when they are lacking in oxygen?
Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) pyruvate can be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide by yeast
(ii) fermentation takes place in the case of aerobic bacteria
(iii) fermentation takes place in mitochondria
(iv) fermentation is a form of anaerobic respiration
Which of the following statements are true about respiration?
(i) during inhalation, ribs move inward and diaphragm is raised.
(ii) the gaseous exchange takes place in the alveoli.
(iii) haemoglobin has greater affinity for carbon dioxide than oxygen.
(iv) alveoli increase surface area of the exchange of gases
The two organisms which breath only through their moist skin are:
There are five animals P, Q, R, S and T. The animal P always lives in water and has gills for breathing. The animal Q can stay in water as well as on land and can breathe both, through moist skin and lungs. The animal R lives in soil and breathes only through its skin. The animal S lives on land and breathes through spiracles and tracheae. And animal T lives in water and breathes through its cell membrane.
(a) Which of the animals could be Amoeba?
(b) Which of the animals could be frog?
(c) Which animal could be fish?
(d) Which animal could be grasshopper?
(e) Which animal could be earthworm?
It has been found that people living in very high mountains have many more red corpuscles in their blood than people living in plains. Which one of the following best accounts for this phenomenon?
There is a pair of bean-shaped organs P in the human body towards the back, just above the waist. A waste product Q formed by the decomposition of unused proteins in the liver is brought into organ P through blood by an artery R. The numerous tiny filters S present in organ P clean the dirty blood by removing the waste product Q. The clean blood goes into circulation through a vein T. The waste substance Q, other waste salts, and excess water form a yellowish liquid U which goes from organ P into a bag-like structure V through two tubes W. This liquid is then thrown out of the body through a tube X.
(a) What is (i) organ P, and (ii) waste substance Q?
(b) Name (i) artery R, and (ii) vein T.
(c) What are tiny filters S known as?
(d) Name (i) liquid U (ii) structure V (iii) tubes W, and (iv) tube X.
Veins and arteries carry blood. Which of these carry blood back to the heart?
Answer this question.
Name the organ of respiration in fishes.
Tick the most appropriate answer.
The products of respiration are :
Choose the odd one out in the following groups of four items each:
Ethyl alcohol, Carbon dioxide, Starch, Oxygen
Name the body structure concerned with the given functional activity:
Combines with the oxygen in the lungs.
Match the items in Column I with the ones most appropriate in Column II. Rewrite the matching pairs.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(a) Alveoli |
(i) where aerobic respiration takes place |
|
(b) Bronchioles |
(ii) lined with hair |
|
(c) Nasal Chamber |
(iii) diffusion of gases |
|
(d) Bronchi |
(iv) small air tubes |
|
(v) an inverted Y shaped tube |
|
|
(vi) a common passage for food and air |
State one function of the following:
Mitochondria
Give suitable explanation for the following :
Why does a person feel breathlessness at higher altitudes?
List the organs of Human respiratory system.
____________ refers to a biochemical process of oxidation of organic compounds in an orderly manner for the liberation of chemical energy in the form of ATP.
______ refers to the physical process by which gaseous exchange takes place between the atmosphere and the lungs.
Sometimes we get painful cramps in our leg muscles after running for a long time due to the accumulation of:
Which is the correct sequence of air passage during inhalation?
How does aerobic respiration differ from anaerobic respiration?
Name the energy currency in the living organisms. When and where is it produced?
Mark the following statement as True or False. Correct the false statement.
Exhaled air has more percentage of CO2 than inhaled air
With the reference to four gases CO2, CO, Cl2 and O2, which one of the options in the table is correct?
Match the correct answers with the type of respiration and respiratory substances.
| Respiration | Types of Substrates |
| A. Floating respiration | I. Proteins |
| B. Cytoplasmic respiration | II. Glucose |
| C. Protoplasmic respiration | III. Carbohydrates and fats |
