Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What do you mean by electron emission? Explain briefly various methods of electron emission.
उत्तर
Electron emission:
- Free electrons possess some kinetic energy and this energy is different for different electrons. The kinetic energy of the free electrons is not sufficient to overcome the surface barrier.
- Whenever additional energy is given to the free electrons, they will have sufficient energy to cross the surface barrier. And they escape from the metallic surface.
-
The liberation of electrons from any surface of a substance is called electron emission.
There are mainly four types of electron emission which are given below.
(i) Thermionic emission: When a metal is heated to a high temperature, the free electrons on the surface of the metal get sufficient energy in the form of thermal energy so that they are emitted from the metallic surface. This type of emission is known as thermionic emission.
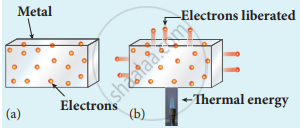
Electrons in the (a) metal (b) heated metal
The intensity of the thermionic emission (the number of electrons emitted) depends on the metal used and its temperature.

Thermionic emission from hot filament of cathode ray tube or x-ray tube
Examples: cathode ray tubes, electron microscopes, X-ray tubes, etc.
(ii) Field emission: Electric field emission occurs when a very strong electric field is applied across the metal. This strong field pulls the free electrons and helps them to overcome the surface barrier of the metal.

Field emission
Examples: Field emission scanning electron microscopes, Field-emission display, etc.
(iii) Photo electric emission: When electromagnetic radiation of suitable frequency is incident on the surface of the metal, the energy is transferred from the radiation to the free electrons. Hence, the free electrons get sufficient energy to cross the surface barrier and the photo electric emission takes place. The number of electrons emitted depends on the intensity of the incident radiation.

Photo electric emission
Examples: Photo diodes, photo electric cells, etc.
(iv) Secondary emission: When a beam of fast-moving electrons strikes the surface of the metal, the kinetic energy of the striking electrons is transferred to the free electrons on the metal surface. Thus the free electrons get sufficient kinetic energy so that the secondary emission of, electron occurs.
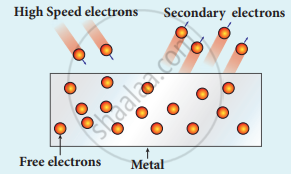
Secondary emission of electrons
Examples: Image intensifies, photo multiplier tubes, etc.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Quarks inside protons and neutrons are thought to carry fractional charges [(+2/3)e; (–1/3)e]. Why do they not show up in Millikan’s oil-drop experiment?
How does one explain the emission of electrons from a photosensitive surface with the help of Einstein's photoelectric equation?
An isolated metal sphere is heated to a high temperature. Will it become positively charged due to thermionic emission?
A diode value is connected to a battery and a load resistance. The filament is heated, so that a constant current is obtained in the circuit. As the cathode continuously emits electrons, does it become more and more positively charged?
Why does thermionic emission not take place in non-conductors?
The constant A in the Richardson−Dushman equation for tungsten is 60 × 104 A m−2K−2. The work function of tungsten is 4.5 eV. A tungsten cathode with a surface area 2.0 × 10−5 m2 is heated by a 24 W electric heater. In steady state, the heat radiated by the heater and the cathode equals the energy input by the heater and the temperature becomes constant. Assuming that the cathode radiates like a blackbody, calculate the saturation current due to thermions. Take Stefan's Constant = 6 × 10−8 W m−2 K−1. Assume that the thermions take only a small fraction of the heat supplied.
Answer the following question.
Define the term "Threshold frequency", in the context of photoelectric emission.
The work function of aluminum is 4⋅2 eV. If two photons each of energy 2⋅5 eV are incident on its surface, will the emission of electrons take place? Justify your answer.
The wavelength λe of an electron and λp of a photon of same energy E are related by
Photoelectric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequencies ν1 and ν2 of the incident light (ν1 > ν2). If the maximum value of kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in the two cases are in the ration 1 : n then the threshold frequency of the metallic surface is ______.
