Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What do you understand by Linear combination of atomic orbitals in MO theory?
उत्तर
The wave functions for the molecular orbitals can be obtained by solving the Schrodinger wave equation for the molecule. Since solving the Schrodinger equation is too complex, approximation methods are used to obtain the wave function for molecular orbitals. The most common method is the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO).
We know that the atomic orbitals are represented by the wave function ψ. Let us consider two atomic orbitals represented by the wave function ψA and ψB with comparable energy, combines to form two molecular orbitals. One is bonding molecular orbital `(ψ_"bonding")` and the other is antibonding molecular orbital `(ψ_"antibonding")` The wave functions for these two molecular orbitals can be obtained by the linear combination of the atomic orbitals ψA and ψB as below,
`(ψ_"bonding") = ψ_"A" + ψ_"B"`;
`(ψ_"antibonding") = ψ_"A" - ψ_"B"`;
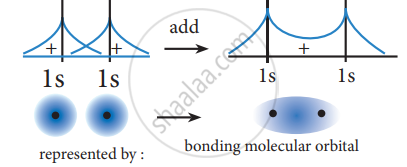
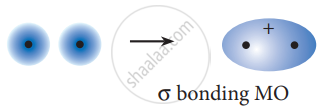
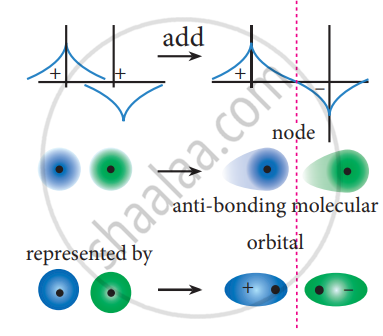
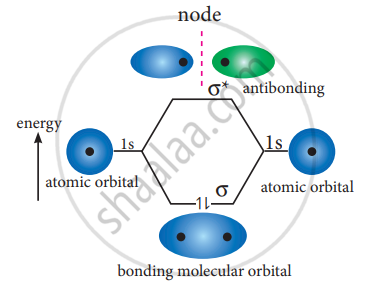
The formation of bonding molecular orbital can be considered as the result of constructive interference of the atomic orbitals and the formation of anti-bonding molecular orbital can be the result of the destructive interference of the atomic orbitals. The formation of the two molecular orbitals from two is orbitals is shown below.
Constructive interaction:
The two 1s orbitals are in phase and have the same sign,
Destructive interaction:
The two orbitals are out phase
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Select and write the most appropriate alternatives from the given choices.
Which molecule is linear?
Select and write the most appropriate alternatives from the given choices.
Which of the following is true for CO2?
Draw an orbital diagram of Hydrogen fluoride molecule
Arrange the following compounds on the basis of lattice energies in decreasing (descending) order:
BeF2, AlCl3, LiCl, CaCl2, NaCl
Hydrogen gas is diatomic whereas inert gases are monoatomic – Explain on the basis of MO theory.
4p, 4d, 5s and 5p orbitals are arranged in the order of decreasing energy. The CORRECT option is:
Which one of the following sets CORRECTLY represents the increase in the paramagnetic property of the ions?
According to MOT, the number of unpaired electrons in O2 molecule is ____________.
According to molecular orbital theory, which of the following will NOT be viable?
H2 molecule is more stable than Li2 molecule, because ______.
