Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is Complement and explain its two types?
उत्तर
There are two types of complement:
- subject complement.
- object complement.
Subject complement is a word or a phrase used after a verb that describes the subject. The underlined words and phrases in the following sentences are subject complements.
- I am hungry.
- My sister became a teacher.
The word ‘hungry’ and the phrase ‘a teacher’ describe the subjects of the verbs. Therefore, they are subject complements.
An object complement comes after the object of a verb and gives us information about the object. The underlined words and phrases in the following sentences are object complements.
- The class made her the monitor.
- The teacher found my answer correct.
The phrase ‘the monitor’ gives us information about the object ‘her’. The word ‘correct’ gives us information about the object ‘my answer’
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Butter milk ____ good for health.
You wouldn't like to invite my Dad, ________.
State which of the following sentence are Compound, and which are Complex.
I called him, but he gave me no answer.
Appropriate suffix to the word with the clues given.
Very pretty ______.
| words | suffixes |
| penny, beauty, develop, teach. | ful, ment, er, less. |
Underline the correct verb in these sentence.
Measles (is, are) very serious.
Fill in the blank with the correct form of the verb given in the bracket.
Evangelene ______ her job a couple of years ago. (quit)
Underline the prepositional phrase.
With reference to your advertisement in a local newspaper, I am applying for the post of a salesman.
______ you help me cross the road, young man?
Join the sentences using appropriate Co-ordinators. (but, or, so, and)
He places his fingers into the master controls. He operates all four arms of the Da vinci.
We have seen that clauses are parts of a sentence, and they are classified as main and subordinate or dependent clauses. Dependent clauses can be further classified as follows according to the work they do in a sentence.
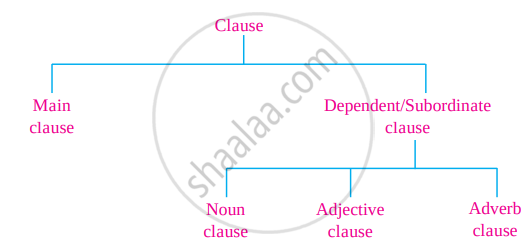
How do we decide whether a clause is a noun clause, an adjective clause or an adverb clause? There is a simple rule - we can replace an adverb clause with an adverb, an adjective clause with an adjective and a noun clause with a noun.
Look at the following examples -
- But I don’t know the answer. (Noun)
But I don’t know what they want. (Noun clause) - He told us a funny story. (Adjective)
He told us a story that was funny. (Adjective clause) - They went away. (Adverb)
They went when you were talking to your friend. (Adverb clause)
Now complete the following on your own :
- But I don’t know ____________.
- He told us ____________.
- They went ____________.
