Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the function of calyx?
उत्तर
The main function of calyx is to protect the inner whorls of the flower.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Match the following:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Stigma | (a) Neuron |
| (ii) Pepsin | (b) Carpel |
| (iii) Dendrites | (c) Protein |
| (d) Stamen |
Answer the following question.
What is pollination? Explain the different types of pollination.
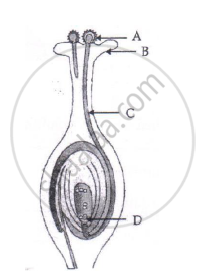
(i) Name the part marked 'A' in the diagram.
(ii) How dose 'A' reachese part 'B'?
(iii) State the importance of the part 'C'.
(iv) What happens to the part marked 'D' after fertilisation is over?
Name and differentiate between the two modes of pollination in flowering plants.
"The chromosomal number of the sexually producing parents and their offspring is the same." Justify this statement.
Mention the changes a flower undergoes after fertilisation.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The female organ of reproduction in the flower is the...........
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The term used to refer to the transfer of pollen from the stamen of one flower to the carpel of another flower of the same species is...........
Draw a neat sketch of the stamen of a flower. Mark in it filament and anther.
What is made in anther of a flower?
How is the process of pollination different from fertilization?
Name the part of a seed which contains stored food.
The correct sequence of reproductive stages occurring in flowering plants is ______
What is a flower ? Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the L.S. of a typical flower.
State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F):
Flowers which possess stamens and carpel are called unisexual.
You have to perform the experiment, "To identify the different parts of an embryo of a gram seed." Describe the procedure that you would follow.
Explain the process of fertilisation in flowers.
A student is asked to study the different parts of an embryo of pea seeds. Given below are the essential steps for the experiment :
(I) Soak the pea seeds in plain water and keep them overnight.
(II) Cut open the soaked seed and observe its different parts.
(III) Take some pea seeds in a petri dish.
(IV) Drain the excess water. Cover the seeds with a wet cotton cloth and leave them as it is for a day.
The correct sequence of these steps is
(A) III, I, IV, II
(B) III, IV, I, II
(C) III, I, II, IV
(D) III, II, I, IV
Explain sexual reproduction in plants.
Answer the following question.
How does suitable pollination lead to fertilization?
Answer the following question.
List two agents of pollination?
Find an odd one out.
Calyx : Sepals : : Corolla : ________________
Write the events involved in the sexual reproduction of a flowering plant.
a. Discuss the first event and write the types.
b. Mention the advantages and the disadvantages of that event.
In which part of the flower germination of pollen grains takes place?
The ovule of an angiosperm is technically equivalent to ______
Which of the following are the chemical components of the wall of pollen tube?
How many middle layers are generally present in the wall of the anther lobes?
Pineapple fruit develops from ______.
What would be the number of chromosomes in the cells of the aleurone layer in a plant species with 8 chromosomes in its synergids?
Pollen grains are produced by ______
Give reason for the following:
Fertilization cannot take place in flowers if pollination does not occur.
Where is the zygote located in the flower after fertilization?
Double fertilization means ______.
Sketch and label the essential and accessory whorls of flower.
In a plant flower the female whorl is ______.
State the post-fertilisation changes that lead to fruit formation in plants.
- Assertion: Primary endosperm nucleus is diploid.
- Reason: It is the product of double fertilisation.
