Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is simple tissue? Classify and explain its different types with suitable diagram.
उत्तर
Simple tissue:
These tissues are composed of structurally and functionally similar cells.
They are of three types.
(i) Parenchyma:
It is widely distributed in plant bodies such as stems, roots, leaves, flowers, and fruits. Its cells are isodiametric and contains live protoplasm. It serves as a food storage and packing tissue. It also stores waste products of plants.

(ii) Collenchyma:
It is located below the epidermis of dicot stem and petiole. It consists of living cells and is characterised by an extra deposition of cellulose at the corners. It is a mechanical tissue in young plants. It also provides elasticity to the plant, particularly stem of dicots.


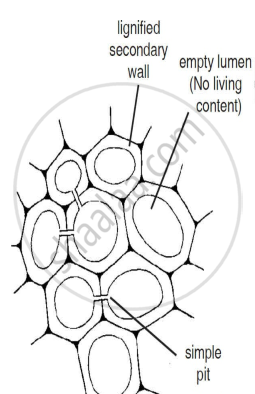
(iii) Sclerenchyma:
It consist of dead lignified cells. It has two types of cells—that is, fibres and sclereids. It occurs in abundance or in patches in definite layers in stems, roots, veins of leaves, hard covering of seeds, and nuts. It provides mechanical support to the plant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Distinguish between tracheids and vessels.
Explain different types of elements present in phloem.
Write the functions of parenchyma, collencyma and sclerenchyma.
Parenchyma containing chloroplasts is known as :
Differentiate between cells of Parenchyma and Collenchyma.
Match the column (A) with the column (B)
| (A) | (B) | ||
| (a) | Parenchyma | (i) | Thin walled, packing cells |
| (b) | Photosynthesis | (ii) | Carbon fixation |
| (c) | Aerenchyma | (iii) | Localized thickenings |
| (d) | Collenchyma | (iv) | Buoyancy |
| (e) | Permanent tissue | (v) | Sclerenchyma |
Name any two simple and two complex permanent tissues in plants.
Match the followings and choose the correct option from below
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Meristem | i. Photosynthesis, storage |
| B. Parenchyma | ii. Mechanical support |
| C. Collenchyma | iii. Actively dividing cells |
| D. Sclerenchyma | iv. Stomata |
| E. Epidermal tissue | v. Sclereids |
Cells of this tissue are living and show angular wall thickening. They also provide mechanical support. The tissue is ______.
