Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth, charges appear on both. A similar phenomenon is observed with many other pairs of bodies. Explain how this observation is consistent with the law of conservation of charge.
उत्तर
The phenomenon of charging by friction is in complete harmony with the law of conservation of charge. When two neutral objects are rubbed in such a phenomenon, both objects get charged. Before friction, both objects are neutral, that is, their total charge is zero. In all such observations, it has always been found that as much positive charge comes on one object, the same negative charge comes on the other object. Thus, even after charging by friction, the net charge of both objects remains zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the meaning of the statement ‘electric charge of a body is quantised’.
Does the charge given to a metallic sphere depend on whether it is hollow or solid? Give reason for your answer.
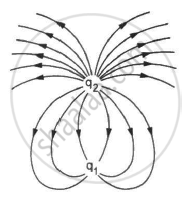
Consider the situation shown in the figure. What are the signs of q1 and q2? If the lines are drawn in proportion to the charges, what is the ratio q1/q2?
A point charge is taken from a point A to a point B in an electric field. Does the work done by the electric field depend on the path of the charge?
Choose the correct option.
Two charges of 1.0 C each are placed one meter apart in free space. The force between them will be
Choose the correct option.
Two-point charges of A = +5.0 μC and B = -5.0 μC are separated by 5.0 cm. A point charge C = 1.0 μC is placed at 3.0 cm away from the centre on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the two point charges. The charge at C will experience a force directed towards
Let x = πR`(("P"^2 - "Q"^2)/2)`, where P, Q and Rare lengths. The physical quantity x is ______.
Charge is quantized means ______.
Eight dipoles of charge of magnitude ± e are placed inside a cube. The total electric flux coming out of the cube will be:-
A glass rod rubbed with silk is used to charge a gold-leaf electroscope and the leaves are observed to diverge. The electroscope thus charged is exposed to X-rays for a short period. Then ______
The dimensions of an atom are of the order of an Angstrom. Thus there must be large electric fields between the protons and electrons. Why, then is the electrostatic field inside a conductor zero?
A paisa coin is made up of Al-Mg alloy and weighs 0.75g. It has a square shape and its diagonal measures 17 mm. It is electrically neutral and contains equal amounts of positive and negative charges.
Treating the paisa coins made up of only Al, find the magnitude of equal number of positive and negative charges. What conclusion do you draw from this magnitude?
Figure represents a crystal unit of cesium chloride, CsCl. The cesium atoms, represented by open circles are situated at the corners of a cube of side 0.40 nm, whereas a Cl atom is situated at the centre of the cube.
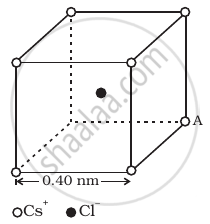
The Cs atoms are deficient in one electron while the Cl atom carries an excess electron.
- What is the net electric field on the Cl atom due to eight Cs atoms?
- Suppose that the Cs atom at the corner A is missing. What is the net force now on the Cl atom due to seven remaining Cs atoms?
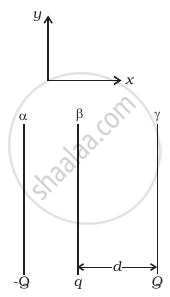
Two fixed, identical conducting plates (α and β), each of surface area S are charged to –Q and q, respectively, where Q > q > 0. A third identical plate (γ), free to move is located on the other side of the plate with charge q at a distance d (Figure). The third plate is released and collides with the plate β. Assume the collision is elastic and the time of collision is sufficient to redistribute charge amongst β and γ.
- Find the electric field acting on the plate γ before collision.
- Find the charges on β and γ after the collision.
- Find the velocity of the plate γ after the collision and at a distance d from the plate β.