Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk cloth, charges appear on both. A similar phenomenon is observed with many other pairs of bodies. Explain how this observation is consistent with the law of conservation of charge.
Solution
The phenomenon of charging by friction is in complete harmony with the law of conservation of charge. When two neutral objects are rubbed in such a phenomenon, both objects get charged. Before friction, both objects are neutral, that is, their total charge is zero. In all such observations, it has always been found that as much positive charge comes on one object, the same negative charge comes on the other object. Thus, even after charging by friction, the net charge of both objects remains zero.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the meaning of the statement ‘electric charge of a body is quantised’.
It is now believed that protons and neutrons (which constitute nuclei of ordinary matter) are themselves built out of more elementary units called quarks. A proton and a neutron consist of three quarks each. Two types of quarks, the so called ‘up’ quark (denoted by u) of charge (+2/3) e, and the ‘down’ quark (denoted by d) of charge (−1/3) e, together with electrons build up ordinary matter. (Quarks of other types have also been found which give rise to different unusual varieties of matter.) Suggest a possible quark composition of a proton and neutron.
A point charge is taken from a point A to a point B in an electric field. Does the work done by the electric field depend on the path of the charge?
When a charged comb is brought near a small piece of paper, it attracts the piece. Does the paper become charged when the comb is brought near it?
In Figure 1 below, a charge Q is fixed. Another charge q is moved along a circular arc MN of radius r around it, from the point M to the point N such that the length of the arc MN = l. The work done in this process is:
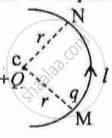
figure 1
Choose the correct option.
Two charges of 1.0 C each are placed one meter apart in free space. The force between them will be
A metallic sphere A isolated from ground is charged to +50 μC. This sphere is brought in contact with other isolated metallics sphere B of half the radius of sphere A. The charge on the two-sphere will be now in the ratio
Answer the following question.
State the law of conservation of charge.
Let x = πR`(("P"^2 - "Q"^2)/2)`, where P, Q and Rare lengths. The physical quantity x is ______.
Conservation of charges in tribo electric charging _________.
The number of lines of force that radiate outwards from one coulomb of charge is:-
A glass rod rubbed with silk is used to charge a gold-leaf electroscope and the leaves are observed to diverge. The electroscope thus charged is exposed to X-rays for a short period. Then ______
Consider a coin of Example 1.20. It is electrically neutral and contains equal amounts of positive and negative charge of magnitude 34.8 kC. Suppose that these equal charges were concentrated in two point charges seperated by (i) 1 cm `(∼ 1/2 xx "diagonal of the one paisa coin")`, (ii) 100 m (~ length of a long 6 building) and (iii) 106 m (radius of the earth). Find the force on each such point charge in each of the three cases. What do you conclude from these results?
A steady current of 8 mA flows through a wire. The number of electrons passing through a cross-section of the wire in 10 s is ______.
