Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When an object is placed 10 cm in front of lens A, the image is real, inverted, magnified and formed at a great distance. When the same object is placed 10 cm in front of lens B, the image formed is real, inverted and same size as the object.
What is the nature of lens A?
उत्तर
Lens A is a converging (convex) lens as only a converging lens forms a real image.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the principal focus of a concave lens.
Where must the object be placed for the image formed by a converging lens to be:
real, inverted and same size as the object?
Copy and complete the diagram below to show what happens to the rays of light when they pass through the concave lens:
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Lenses refract light to form images: a..................... lens can form both real and virtual images, but a diverging lens forms only ...................... images.
State one practical use each of convex mirror, concave mirror, convex lens and concave lens.
A concave lens of 20 cm focal length forms an image 15 cm from the lens. Compute the object distance.
Give two characteristic of the image formed by a concave lens.
The diagrams showing the correct path of the ray after passing through the lens are:
 |
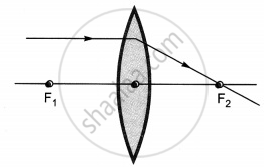 |
| I | II |
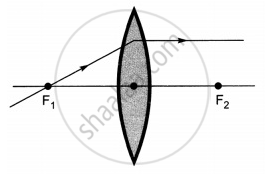 |
 |
| III | IV |
Distinguish between concave and convex lens.
Do we expect any change in the position, nature, and size of the image
(i) formed by a concave lens,
(ii) with a change in the position of the object?
