Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When is the work done by a force on a body : (a) positive, (b) negative, and (c) zero?
उत्तर
(a) Positive work – Work done is positive when the force aplied and the displacement caused are in same direction.
Example: When we kick a football, it moves in the direction of the force applied and hence, the work done in this case is positive.
(b) Negative work – Work done is negative when the force applied and the displacement caused are in opposite direction.
Example: Work done by the frictional force on a rolling football to decrease its motion is an example of negative work, as the direction of frictional force (acting on the ball) is opposite to the direction of the football’s motion
(c) Zero work – Work done can be zero for the following two reasons:
1. The displacement is zero.
2. The force and displacement are perpendicular to each other.
Work done by the earth on a satellite moving around the earth is zero as the direction of the motion of the satellite is always perpendicular to the direction of the gravitational force.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
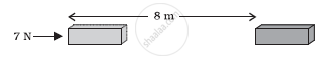
A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force (see the given figure). Let us take it that the force acts on the object through the displacement. What is the work done in this case?
Name a common device where a gear train is used
State the S.I. unit of energy.
Find the kinetic energy of a body of mass 1 kg moving with a uniform velocity of 10 m s-1.
A bullet of mass 0.5 kg slows down from a speed of 5 m s-1 to that of 3 m s-1. Calculate the change in kinetic energy of the ball.
What happens to the work done when the dispacement of body is at right angles to the direction of force acting on it? Explain your answer.
What is the work done against gravity when a body is moved horizontally along a frictionless surface?
On what factors does the work done by a force depend?
Distinguish between work and power.
A weight lifted a load of 200 kgf to a height of 2.5 m in 5 s. calculate: (i) the work done, and (ii) the power developed by him. Take g= 10 N kg-1.
Name the physical quantity whose MKS units are kgm2s-3.
Calculate the amount of work done by a child carrying a bag of 20 kg when he moves a distance of 40 m in
(a) Vertical direction, and
(b) Horizontal direction
Define energy and state the unit of energy and the law of conservation of energy.
Name two places in India where electricity is generated from nuclear power plants.
A water pump raises 50 kg of water through a height of 25 m in 5s. Calculate the power supplied by the pump (Take: g = 10 N kg−1).
A force of F = (5y + 20) `hat"j"` N acts on a particle. The work done by this force when the particle is moved from y = 0 m to y = 10 m is ______ J.
