Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
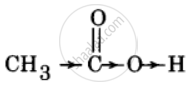
CH3CO2H or CH2FCO2H
उत्तर
|
It is difficult for the proton to escape because the +I effect of −CH3 group increases the electron density in the O–H bond. |
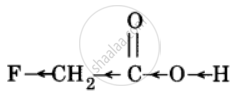
The release of the proton is easy because the −I effect of −F reduces the electron density in the O–H bond. |
|
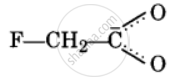
The +I effect due to the concentration of negative charge destabilises the carboxylate ion. |
The spreading of the negative charge causes the –I effect to stabilize the carboxylate ion. |
Hence, due to lower electron density in the O–H bond and higher stability of FCH2COO– ion, FCH2COOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How is 1-nitropropane prepared from suitable oxime?
Why pKa of F-CH2-COOH is lower than that of Cl−CH2−COOH?
Which acid of the pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
Which acid of the pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
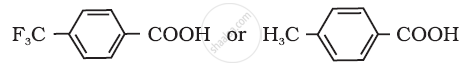
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH, CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH, CH3CH2CH2COOH (acid strength)
Write the reactions involved Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction?
Account for the following:
Carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
What happens when Salicylic acid is treated with (CH3CO)2 O/H+?
Assertion: Formaldehyde is a planar molecule.
Reason: It contains sp2 hybridised carbon atom.
Acidity of BF3 can be explained on the basis of which of the following concepts?
When propionamide reacts with Br2 in the presence of alkali the product is ______.
Na2CO3 cannot be used in place of (NH4)2CO3 for the precipitation of the V group because ______.
Formic acid and formaldehyde can be distinguished by treating with ______.
Describe the action of alcoholic potassium hydroxide (alc. KOH) on ethyl bromide
Describe the action of alcoholic potassium hydroxide (alc. KOH) on n-propyl bromide