Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following have zero average value in a plane electromagnetic wave?
(a) Electric field
(b) Magnetic field
(c) Electric energy
(d) Magnetic energy
उत्तर
(a) Electric field
(b) Magnetic field
In a plane electromagnetic wave, the electric and the magnetic fields oscillate sinusoidally. For an electromagnetic wave propagating in the z-direction, the electric and magnetic fields are given by:
Ex = E0 sin (kz – ωt)
By = B0 sin (kz – ωt)
These are sinusoidal functions. Therefore, for a fixed value of z, the average value of the electric and magnetic fields are zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Suppose that the electric field amplitude of an electromagnetic wave is E0 = 120 N/C and that its frequency is v = 50.0 MHz.
- Determine B0, ω, k, and λ.
- Find expressions for E and B.
How is the speed of em-waves in vacuum determined by the electric and magnetic field?
How are the magnitudes of the electric and magnetic fields related to velocity of the em wave?
Write the following radiations in ascending order with respect to their frequencies:
X-rays, microwaves, UV rays and radio waves.
The energy contained in a small volume through which an electromagnetic wave is passing oscillates with
Which of the following electromagnetic radiations is used for viewing objects through fog ______.
Let E = E0 sin[106 x -ωt] be the electric field of plane electromagnetic wave, the value of ω is ______.
What are electromagnetic waves?
Why are e.m. waves non-mechanical?
Explain the types of absorption spectrum.
A transmitter consists of LC circuit with an inductance of 1 μH and a capacitance of 1 μF. What is the wavelength of the electromagnetic waves it emits?
The velocity of light in vacuum can be changed by changing
If `vecE` and `vecB` represent electric and magnetic field vectors of the electromagnetic wave, the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave is along ______.
The source of electromagnetic waves can be a charge ______.
- moving with a constant velocity.
- moving in a circular orbit.
- at rest.
- falling in an electric field.
Even though an electric field E exerts a force qE on a charged particle yet the electric field of an EM wave does not contribute to the radiation pressure (but transfers energy). Explain.
An infinitely long thin wire carrying a uniform linear static charge density λ is placed along the z-axis (figure). The wire is set into motion along its length with a uniform velocity `v = vhatk_z`. Calculate the poynting vector `S = 1/mu_0 (E xx B)`.
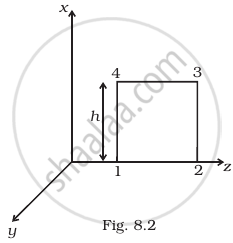
A plane EM wave travelling in vacuum along z direction is given by `E = E_0 sin(kz - ωt)hati` and `B = B_0 sin(kz - ωt)hatj`
- Evaluate `oint E.dl` over the rectangular loop 1234 shown in figure.
- Evaluate `int B.ds` over the surface bounded by loop 1234.
- Use equation `oint E.dl = (-dphi_B)/(dt)` to prove `E_0/B_0` = c.
- By using similar process and the equation `ointB.dl = mu_0I + ε_0 (dphi_E)/(dt)`, prove that c = `1/sqrt(mu_0ε_0)`
For an electromagnetic wave travelling in free space, the relation between average energy densities due to electric (Ue) and magnetic (Um) fields is ______.
An electromagnetic wave of frequency 3 GHz enters a dielectric medium of relative electric permittivity 2.25 from vacuum. The wavelength of this wave in that medium will be ______ × 10-2 cm.
An electromagnetic wave of frequency v = 3.0 MHz passes from vacuum into a dielectric medium with permittivity ∈ = 4.0. Then ______.
