Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which property of light does not change when it travels from one medium to another?
The property of light which does not change, when it travels from one medium to another is ______.
पर्याय
Velocity
Wavelength
Amplitude
Frequency
उत्तर १
Frequency
Explanation:
When the light passes from one medium to another, the property called refraction occurs. This refraction is the bending of light at the interface of two mediums. This bending would further result in a change in velocity, amplitude and wavelength. The frequency of the light wave is a parameter of the source that it emits from. It does not depend on the medium of propagation.
उत्तर २
The property of light which does not change, when it travels from one medium to another is frequency.
संबंधित प्रश्न
When wavelength of light used in optic I instruments A and Bare 4500 Å and 6000 Å respectively, the ratio of resolving pow of A to B will be ______.
Refractive index of the medium isµ and wavelength is λ, then which of the following proportionality relation is correct?
A thin hollow prism of refracting angle 3°, filled with water gives a deviation of 1°. The refractive index of water is ______.
Glass has refractive index μ with respect to air and the critical angle for a ray of light going from glass to air is θ. If a ray of light is incident from air on the glass with angle of incidence θ corresponding angle of refraction is ______.
The refractive index of the material of crystal is 1.68 and that of castor oil is 1.2. When a ray of light passes from oil to glass, its velocity will change by a factor ______.
Consider a light ray travelling in air is incident into a medium of refractive index `sqrt(2"n")`. The incident angle is twice that of refracting angle. Then, the angle of incidence will be ______.
A parallel beam of light of wavelength 900 nm and intensity 100 wm-2 is incident on a surface perpendicular to the beam. The number of photons crossing 1 cm2 area perpendicular to the beam in one second is ______
Which is the correct ascending order of wavelengths?
A ray of light is incident normally on a glass slab of thickness 5 cm and refractive index 1.6. The time taken to travel by a from source of slab is same as to travel through glass slab. The distance of source from the surface is ______.
A vessel of depth 2d cm is half filled with a liquid of refractive index μ1 and the upper half with liquid of refractive index μ2, the apparent depth as seen normally is ______.
A point source S is placed at the bottom of a transparent block of height 10 mm and refractive index 2.72. It is immersed in a lower refractive index liquid as shown in the figure. It is found that the light emerging from the block to the liquid forms a circular bright spot of diameter 11.54 mm on the top of the block. The refractive index of the liquid is ______.
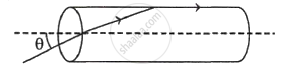
A transparent solid cylindrical rod has a refractive index of 2/`sqrt3`. It is surrounded by air. A light ray is incident at the mid point of one end of the rod as shown in the figure.
The incident angle θ for which the light ray grazes along the wall of the rod is ______.
Light of wavelength 6000 Å incident on a single slit. The first minimum of the diffraction pattern is obtained at 4 min from the centre. The screen is at a distance of 2m from the silt. The slit width will be ______.
A beam of light is travelling from region II to region III (see the figure). The refractive index in the region I, II and III are n0, `"n"_0/sqrt2` and `"n"_0/sqrt2` respectively. The angle of incidence θ for which the beam just misses entering region III is ______.
| Region I | Region II | Region III |
 |
||
| n0 | n0`sqrt2` | n0`sqrt2` |
A beaker contains water up to a height h1 and kerosene of height h2 above water, so that the total height of (water + kerosene) is (h1 + h2). Refractive index of water is μ1 and that of kerosene is μ2. The apparent shift in the position of the bottom of the beaker when viewed from above is ______.
A ball is dropped from a height of 20 m above the surface of water in a lake. The refractive index of water is 4/3. A fish inside the lake, in the line of fall of the ball is looking at the ball. At an instant, when the ball is 12.8 m above the water surface, the fish sees the speed of ball as ______.
In a double-slit experiment using monochromatic light, the fringe pattern shifts by a certain distance on the screen when a mica sheet with a refractive index of 1.6 and thickness of 1.964 µm covers one of the slits. The mica sheet is then removed and the slits-to-screen distance is doubled so that the new fringe width is the same as the observed fringe shift with the mica sheet. Calculate the wavelength of the monochromatic light used.
A ray of light is incident on a water surface of refractive index `4/3` making an angle of 40° with the surface. Find the angle of refraction.
When a monochromatic light passes through a slit 0.2 mm wide and falls on a screen 3.5 m away, the first minimum of the diffraction pattern is 9.1 mm from the centre of the central maximum. The wavelength of the light is ______.
