Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why do you think the zygote is dormant for sometime in a fertilised ovule?
उत्तर
After fertilisation, the zygote develops in the ovule. The integuments of the ovule harden and form the seed coat. The outer integument of the ovule forms the seed coat and the inner integument forms the inner coat. Food materials start getting accumulated in the endosperm. The amount of water gradually decreases, hence, the soft ovule becomes hard and dry. Gradually, the functional activities inside the ovule stop and the new embryo formed from the zygote reaches a dormant state. This is called zygote dormancy. This structure surrounded by seed coat, containing the accumulated food and dormant embryo is called seed.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Read the following statement and answer the questions that follow :
"A guava fruit has 200 viable seeds."
(a) What are viable seeds?
(b) Write the total number of :
(i) Pollen grains (ii) Gametes
in producing 200 viable guava seeds.
c) Prepare a flow-chart to depict the post-pollination events leading to viable-seed production in a flowering plant.
Triple Fusion involves:
(i) Fusion of one male, gamete with female gamete
(ii) Fusion of tube nucleus with generative nvcleus
(iii) Fusion of two polar nuclei.
(iv) Fusion of second male gamete with two polar nuclei
Describe any two devices in a flowering plant which prevent both autogamy and geitonogamy.
During double fertilization second male gamete fuses with ___________.
Explain the Following Term:
Ornithophily
Explain the following term:
Elephophily
What happens to the following after fertilization?
Stamens
What are the advantages of the following in the flower to the plant concerned?
Smooth and light pollen
What is the function of the pollen tube? Explain it with the help of a diagram.
Given ahead is a diagrammatic representation of the process of fertilization. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
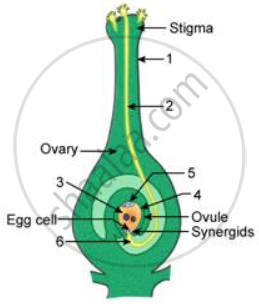
What happens to
i) Ovary
ii) Ovule after fertilisation
What is ‘double fertilization’? Describe it with the help of a neat and well-labeled diagram. Give its importance.
Define fertilization.
Explain double fertilization and its significance.
What is a fruit?
What happens to the ovary post fertilization?
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
One male gamete fuses with the egg and forms a diploid zygote. This process is called
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
When only ovary forms fruits they are known as
The seed is a fertilized _______.
After fertilization the ovule becomes ______.
Transmitting tissue is found in
In majority of plants pollen is liberated at
Pollen tube was discovered by
Which of the following is the CORRECT sequence of events during double fertilization in Angiosperms?
In double fertilization, the first male gamete fuses with the egg and the second male gan1ete fuses with which of the following?
What would be the number of chromosomes in the megaspore mother cell of the plant if an endosperm of an angiosperm has 24 chromosomes?
Following diagram represents double fertilization. Identify the INCORRECT label.
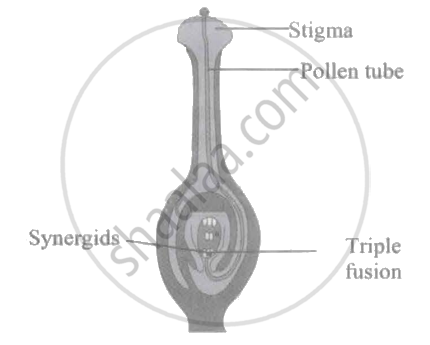
Double fertilisation was first discovered in 1898 by ______ in Fritillaria and Lilium.
The total number of nuclei involved in double fertilisation in angiospersm are ______.
After fertilization, the seed coat of seeds develops from ______
All the events from pollen deposition on the stigma until pollen tubes enter the ovules are together referred to as ______.
Name the part of gynoecium that determines the compatible nature of pollen.
In the diagram given below, show the path of a pollen tube from the pollen on the stigma into the embryo sac. Name the components of egg apparatus.
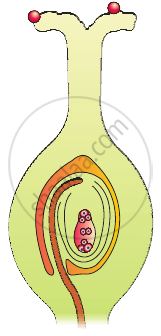
Can an unfertilised, apomictic embryo sac give rise to a diploid embryo? If yes, then how?
What is the function of the two male gametes produced by each pollen grain in angiosperms?
Name the following:
A diploid nucleus in central cell of embryo sac in plants.
Give a term for the following:
Fusion of male gamete and secondary nucleus in angiosperms.
