Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why do you think the zygote is dormant for sometime in a fertilised ovule?
Solution
After fertilisation, the zygote develops in the ovule. The integuments of the ovule harden and form the seed coat. The outer integument of the ovule forms the seed coat and the inner integument forms the inner coat. Food materials start getting accumulated in the endosperm. The amount of water gradually decreases, hence, the soft ovule becomes hard and dry. Gradually, the functional activities inside the ovule stop and the new embryo formed from the zygote reaches a dormant state. This is called zygote dormancy. This structure surrounded by seed coat, containing the accumulated food and dormant embryo is called seed.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is triple fusion?
During double fertilization second male gamete fuses with ___________.
Match the items in Column A with those in Column B.
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(a) Generative nucleus |
(i) Pollen tube |
|
(b) Germ pore |
(ii) Endosperm nucleus |
|
(c) Exine |
(iii) Testa |
|
(d) Secondary nucleus |
(iv) Fertilization |
|
(e) Integument |
(v) Male nuclei |
|
(f) Egg nucleus |
(vi) Rough |
Explain the following term:
Elephophily
What happens to the following after fertilization?
Stamens
What are the advantages of the following in the flower to the plant concerned?
Protruding and easily movable anthers
What are the advantages of the following in the flower to the plant concerned?
Fragrant nectar
Given ahead is a diagrammatic sketch of the sectional view of a germinating pollen grain. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
What is the function of the part labelled '4'?
Given ahead is a diagrammatic sketch of the sectional view of a germinating pollen grain. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
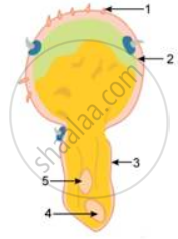
What happens to the part labelled '5' during the process?
Given ahead is a diagrammatic representation of the process of fertilization. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
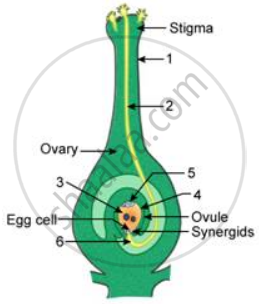
Name the parts labelled 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6.
What is the significance of the dispersal of seeds? Give any two points.
Define fertilization.
What is the function of pollen tube? Explain with the help of a diagram.
What happens to the ovary post fertilization?
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
The study of fruits is known as
Even though each pollen grain has 2 male gametes, why at least 20 pollen grains are required to fertilize 20 ovules in a particular carpel?
Why fertilization process in angiosperms is called as double fertilization?
Describe the process of double fertilization in angiosperms and add a note on its significance.
Size of pollen grain in Myosotis
Match the following
| I) | External fertilization | i) | pollen grain |
| II) | Androecium | ii) | anther wall |
|
III) |
Male gametophyte | iii) | algae |
| IV) | Primary parietal layer | iv) | stamens |
Male gametes in angiosperms are formed by the division of ______.
In majority of plants pollen is liberated at
Define triple fusion.
‘Pollination in Gymnosperms is different from Angiosperms’ – Give reasons.
Write a short note on Heterostyly.
Which of the following happens during triple fusion?
By which of the following the megasporangium proper of an angiosperm ovule is represented?
Due to which of the following reasons the pollen tube usually grows down towards the egg?
Identify the function of filiform apparatus.
From the following identify the fate of the male gametes discharged in the synergid.
If the cells of the nucellus in the angiosperm ovule contain 24 chromosomes, then ____________ chromosomes will be present in the endosperm of a self-pollinated flower.
Through which route the pollen tube can enter the ovule?
In a fertilised embryo sac, the haploid, diploid, and triploid structures are ______.
The total number of nuclei involved in double fertilisation in angiospersm are ______.
Identity the part of embryo sac which takes part in formation of primary endosperm nucleus during fertlisation
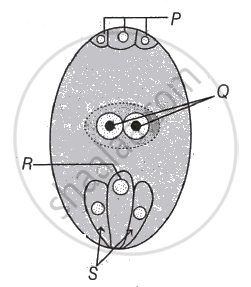
Name the nuclei involved in triple fusion.
