Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Where and how does triple fusion take place?
Solution
Since two types of fusions, syngamy and triple fusion, take place in an embryo sac the phenomenon is termed double fertilisation, an event unique to flowering plants. The central cell after triple fusion becomes the primary endosperm cell (PEC) and develops into the endosperm, while the zygote develops into an embryo.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Read the following statement and answer the questions that follow :
"A guava fruit has 200 viable seeds."
(a) What are viable seeds?
(b) Write the total number of :
(i) Pollen grains (ii) Gametes
in producing 200 viable guava seeds.
c) Prepare a flow-chart to depict the post-pollination events leading to viable-seed production in a flowering plant.
Explain the events up to double fertilisation after the pollen tube enters one of the synergids in an ovule of an angiosperm.
Differentiate between outbreeding and outcrossing.
(a) Explain the events after pollination leading to the formation of a seed in angiosperms.
(b) Mention the ploidy levels of the cells of different parts of an albuminous seed.
Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
Transference of pollen grains from anthers to stigma of the same flower is called ________.
Match the items in Column A with those in Column B.
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(a) Generative nucleus |
(i) Pollen tube |
|
(b) Germ pore |
(ii) Endosperm nucleus |
|
(c) Exine |
(iii) Testa |
|
(d) Secondary nucleus |
(iv) Fertilization |
|
(e) Integument |
(v) Male nuclei |
|
(f) Egg nucleus |
(vi) Rough |
Name of the part of the ovary which gives rise to:
Seed ______
Explain the Following Term:
Ornithophily
What happens to the following after fertilization?
Calyx
What are the advantages of the following in the flower to the plant concerned?
Fragrant nectar
Given ahead is a diagrammatic sketch of the sectional view of a germinating pollen grain. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
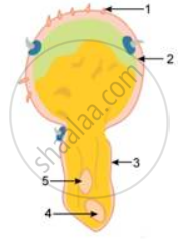
Where does the germination of the pollen grain take place and how?
Given ahead is a diagrammatic representation of the process of fertilization. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
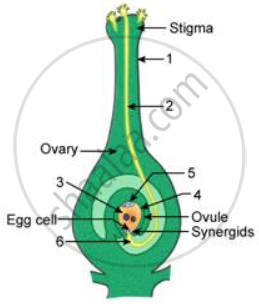
What happens to
i) Ovary
ii) Ovule after fertilisation
What is ‘double fertilization’? Describe it with the help of a neat and well-labeled diagram. Give its importance.
Define fertilization.
Do you think fruits are important for the plant?
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
When only ovary forms fruits they are known as
Size of pollen grain in Myosotis
Syngamy results in the formation of ______.
Male gametes in angiosperms are formed by the division of ______.
What is Mellitophily?
Write a short note on Heterostyly.
Explain the development of a Dicot embryo
Which of the following happens during triple fusion?
In double fertilization, the first male gamete fuses with the egg and the second male gan1ete fuses with which of the following?
The success of seed plants on land is mainly due to ______.
In angiosperms, for formation of which of the following triple fusion is necessary?
By which of the following double fertilization is exhibited?
What would be the number of chromosomes in the megaspore mother cell of the plant if an endosperm of an angiosperm has 24 chromosomes?
If the cells of the nucellus in the angiosperm ovule contain 24 chromosomes, then ____________ chromosomes will be present in the endosperm of a self-pollinated flower.
The total number of nuclei involved in double fertilisation in angiospersm are ______.
All the events from pollen deposition on the stigma until pollen tubes enter the ovules are together referred to as ______.
Can an unfertilised, apomictic embryo sac give rise to a diploid embryo? If yes, then how?
Identity the part of embryo sac which takes part in formation of primary endosperm nucleus during fertlisation
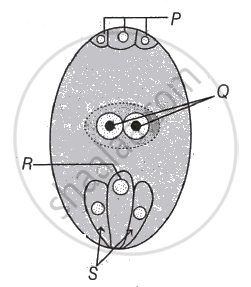
Select the option that shows the correctly identified 'U', 'X', 'Y' and 'Z' in a developing dicot embryo.

Name the following:
A diploid nucleus in central cell of embryo sac in plants.
