Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why must electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor be normal to the surface at every point? Give reason?
उत्तर
Electric field is defined to be the gradient of potential and the surface of a conductor has a constant potential. Therefore, there is no field along the surface of the conductor and, hence, the electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor should be normal to the surface at every point.
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the amount of work done in moving a point charge Q around a circular arc of radius ‘r’ at the centre of which another point charge ‘q’ is located?
The field lines of a negative point charge are as shown in the figure. Does the kinetic energy of a small negative charge increase or decrease in going from B to A?
The bob of a simple pendulum has a mass of 40 g and a positive charge of 4.0 × 10−6 C. It makes 20 oscillations in 45 s. A vertical electric field pointing upward and of magnitude 2.5 × 104 NC−1 is switched on. How much time will it now take to complete 20 oscillations?
A charged oil drop weighing 1.6 x 10-15 N is found to remain suspended in a uniform electric field of intensity 2 x 103 Nc-1. Find the charge on the drop.
A hemisphere is uniformly charged positively. The electric field at a point on a diameter away from the centre is directed ______.
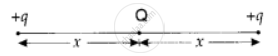
A charge Q is placed at the centre of the line joining two point charges +q and +q as shown in the figure. The ratio of charges Q and q is ______.
Consider two identical point charges located at points (0, 0) and (a, 0).
Is there a point on the line joining them at which the electric field is zero?
An isolated point charge particle produces an electric field `vecE` at a point 3 m away from it. The distance of the point at which the field is `vecE/4` will be ______.
In case of an infinite line charge, how does intensity of electric field at a point change, if at all, when.
- charge on it is doubled?
- distance of the point is halved?
