Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The bob of a simple pendulum has a mass of 40 g and a positive charge of 4.0 × 10−6 C. It makes 20 oscillations in 45 s. A vertical electric field pointing upward and of magnitude 2.5 × 104 NC−1 is switched on. How much time will it now take to complete 20 oscillations?
उत्तर
Given:
Charge of the particle, q = 4.0 × 10−6 C
Electrical field intensity, E = 2.5 × 104 NC−1
Mass of the particle, m = 40 g = 0.04 kg
When no electrical field is applied,
time period,
\[T_1 = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{l}{g}}\]
When upward electrical field is applied,
time period,
\[T_2 = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{l}{g - a}}\],
where a is the upward acceleration due to electrical field, which is given by
\[a = \frac{qE}{m}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \frac{4 \times {10}^{- 6} \times 2 . 5 \times {10}^4}{40 \times {10}^{- 3}}\]
\[ = 2 . 5 \text{m/ s}^2 \]
\[\therefore \frac{T_2}{T_1} = \sqrt{\frac{g}{g - a}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{T_2}{T_1} = \sqrt{\frac{9 . 8}{9 . 8 - 2 . 5}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow T_2 = 45 \times \sqrt{\frac{9 . 8}{7 . 3}} = 52 \] s
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A charge is distributed uniformly over a ring of radius 'a'. Obtain an expression for the electric intensity E at a point on the axis of the ring. Hence, show that for points at large distance from the ring, it behaves like a point charge.
What is the function of uniform radial field and how is it produced?
Why must electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor be normal to the surface at every point? Give reason?
The intensity of the electric field at a point at a perpendicular distance ‘r’ from an infinite line charge, having linear charge density ‘λ’ is given by:
A charged oil drop weighing 1.6 x 10-15 N is found to remain suspended in a uniform electric field of intensity 2 x 103 Nc-1. Find the charge on the drop.
A solid sphere of radius R has a charge Q distributed in its volume with a charge density ρ = kra, where k and a are constants and r is the distance from its centre. If the electric field at r = `"R"/2` is `1/8` times that at r = R, the value of a is ______.
A particle of charge q and mass m moves rectilinearly under the action of electric field E = A – Bx, where A and B are positive constants and x is distance from the point where particle was initially at rest then the distance traveled by the particle before coming to rest and acceleration of particle at that moment are respectively.
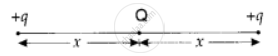
A charge Q is placed at the centre of the line joining two point charges +q and +q as shown in the figure. The ratio of charges Q and q is ______.
Electric field at a point varies as r° for ______.
Electric lines of force about negative point charge are ______
A charge of 4 × 10- 9c is distributed uniformly over the circumference of a conducting ring of radius 0.3 m. Calculate the field intensity at a point on the axis of the ring at 0.4 m from its center and also at the center?
Two equal point charges of the same sign are fixed on the y-axis, on either side of the origin equidistant from it, with the distance between them d. A third charge moves along the x-axis. The distance of the third charge from either of the two fixed charges when force on the third charge is maximum will be ______ cm.
[d = 10 cm]
Consider two identical point charges located at points (0, 0) and (a, 0).
Is there a point on the line joining them at which the electric field is zero?
Consider two identical point charges located at points (0, 0) and (a, 0).
Is there a point on the line joining them at which the electric potential is zero?
An isolated point charge particle produces an electric field `vecE` at a point 3 m away from it. The distance of the point at which the field is `vecE/4` will be ______.
In case of an infinite line charge, how does intensity of electric field at a point change, if at all, when.
- charge on it is doubled?
- distance of the point is halved?
