Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A block of mass m with a charge q is placed on a smooth horizontal table and is connected to a wall through an unstressed spring of spring constant k, as shown in the figure. A horizontal electric field E, parallel to the spring, is switched on. Find the amplitude of the resulting SHM of the block. 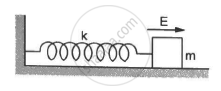
उत्तर
Given:
Charge of the block = q
Electrical field intensity = E
Mass of the block = m
Spring constant = k
Electric force, F = qE
Spring force, F = − kx (where x is the amplitude)
Therefore, qE = − kx
\[\Rightarrow x = \left| - \frac{qE}{k} \right| = \frac{qE}{k}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that if we connect the smaller and the outer sphere by a wire, the charge q on the former will always flow to the latter, independent of how large the charge Q is.
Consider a system of n charges q1, q2, ... qn with position vectors `vecr_1,vecr_2,vecr_3,...... vecr_n`relative to some origin 'O'. Deduce the expression for the net electric field`vec E` at a point P with position vector `vecr_p,`due to this system of charges.
Can a gravitational field be added vectorially to an electric field to get a total field?
The electric field at the origin is along the positive x-axis. A small circle is drawn with the centre at the origin, cutting the axes at points A, B, C and D with coordinates (a, 0), (0, a), (−a, 0), (0, −a), respectively. Out of the points on the periphery of the circle, the potential is minimum at
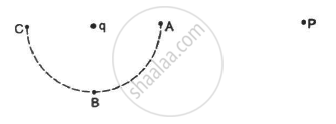
Consider the situation in the figure. The work done in taking a point charge from P to Ais WA, from P to B is WB and from P to C is WC.
A 10-cm long rod carries a charge of +50 μC distributed uniformly along its length. Find the magnitude of the electric field at a point 10 cm from both ends of the rod.
A particle of mass m and charge q is thrown at a speed u against a uniform electric field E. How much distance will it travel before coming to momentary rest ?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. How long will it take for the particle to travel a distance of 40 cm?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. What will be the speed of the particle after travelling this distance?
Consider the situation of the previous problem. A charge of −2.0 × 10−4 C is moved from point A to point B. Find the change in electrical potential energy UB − UA for the cases (a), (b) and (c).
An electric field \[\vec{E} = ( \vec{i} 20 + \vec{j} 30) {NC}^{- 1}\] exists in space. If the potential at the origin is taken to be zero, find the potential at (2 m, 2 m).
Assume that each atom in a copper wire contributes one free electron. Estimate the number of free electrons in a copper wire of mass 6.4 g (take the atomic weight of copper to be 64 g mol−1).
Two identical blocks are kept on a frictionless horizontal table connected by a spring of stiffness k and of original length l0. A total charge Q is distributed on the block such that maximum elongation of spring at equilibrium is equal to x. Value of Q is ______.
In general, metallic ropes are suspended on the carriers taking inflammable materials. The reason is ______.
