Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
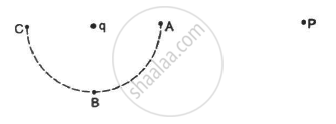
Consider the situation in the figure. The work done in taking a point charge from P to Ais WA, from P to B is WB and from P to C is WC.
पर्याय
WA < WB < WC
WA > WB > WC
WA = WB = WC
None of these
उत्तर
WA = WB = WC
Points A, B and C lie at the same distance from the charge q, i.e. they are lying on an equipotential surface. So, work done in moving a charge from A to B (WAB) or B toC (WBC) is zero.
Hence, work done in bringing a charge from P to A = WA,
from P to B, WB = WA+WAB = WA
and from P to C, WC = WA + WAB + WBC = WA
Hence, WA = WB = WC
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In some old texts it is mentioned that 4π lines of force originate from each unit positive charge. Comment on the statement in view of the fact that 4π is not an integer.
When the separation between two charges is increased, the electric potential energy of the charges
The electric field at the origin is along the positive x-axis. A small circle is drawn with the centre at the origin, cutting the axes at points A, B, C and D with coordinates (a, 0), (0, a), (−a, 0), (0, −a), respectively. Out of the points on the periphery of the circle, the potential is minimum at
If a body is charged by rubbing it, its weight
A 10-cm long rod carries a charge of +50 μC distributed uniformly along its length. Find the magnitude of the electric field at a point 10 cm from both ends of the rod.
A wire is bent in the form of a regular hexagon and a total charge q is distributed uniformly on it. What is the electric field at the centre? You may answer this part without making any numerical calculations.
A particle of mass m and charge q is thrown at a speed u against a uniform electric field E. How much distance will it travel before coming to momentary rest ?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. How long will it take for the particle to travel a distance of 40 cm?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. What will be the speed of the particle after travelling this distance?
A ball of mass 100 g and with a charge of 4.9 × 10−5 C is released from rest in a region where a horizontal electric field of 2.0 × 104 N C−1 exists. (a) Find the resultant force acting on the ball. (b) What will be the path of the ball? (c) Where will the ball be at the end of 2 s?
The kinetic energy of a charged particle decreases by 10 J as it moves from a point at potential 100 V to a point at potential 200 V. Find the charge on the particle.
Find the magnitude of the electric field at the point P in the configuration shown in the figure for d >> a.
The surface charge density of a thin charged disc of radius R is σ. The value of the electric field at the center of the disc is `sigma/(2∈_0)`. With respect to the field at the center, the electric field along the axis at a distance R from the center of the disc ______.
Consider a region inside which, there are various types of charges but the total charge is zero. At points outside the region ______.
In general, metallic ropes are suspended on the carriers taking inflammable materials. The reason is ______.
When 1014 electrons are removed from a neutral metal sphere, the charge on the sphere becomes ______.
The Electric field at a point is ______.
- always continuous.
- continuous if there is no charge at that point.
- discontinuous only if there is a negative charge at that point.
- discontinuous if there is a charge at that point.
Five charges, q each are placed at the corners of a regular pentagon of side ‘a’ (Figure).
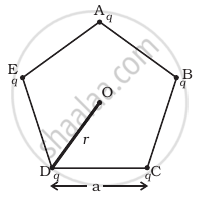
(a) (i) What will be the electric field at O, the centre of the pentagon?
(ii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge from one of the corners (say A) is removed?
(iii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge q at A is replaced by –q?
(b) How would your answer to (a) be affected if pentagon is replaced by n-sided regular polygon with charge q at each of its corners?
