Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A wire is bent in the form of a regular hexagon and a total charge q is distributed uniformly on it. What is the electric field at the centre? You may answer this part without making any numerical calculations.
उत्तर
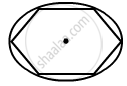
As the wire is bent to form a regular hexagon, it forms an equipotential surface, as shown in the figure.
Hence, the charge at each point is equal and the net electric field at the centre is 0 .
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that if we connect the smaller and the outer sphere by a wire, the charge q on the former will always flow to the latter, independent of how large the charge Q is.
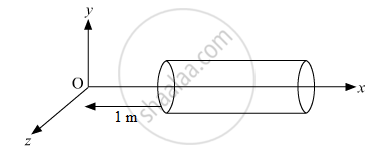
A hollow cylindrical box of length 1 m and area of cross-section 25 cm2 is placed in a three dimensional coordinate system as shown in the figure. The electric field in the region is given by `vecE = 50xhati` where E is NC−1 and x is in metres. Find
(i) Net flux through the cylinder.
(ii) Charge enclosed by the cylinder.
Why does a phonograph record attract dust particles just after it is cleaned?
When the separation between two charges is increased, the electric potential energy of the charges
If a body is charged by rubbing it, its weight
The electric field and the electric potential at a point are E and V, respectively.
Electric potential decreases uniformly from 120 V to 80 V, as one moves on the x-axis from x = −1 cm to x = +1 cm. The electric field at the origin
(a) must be equal to 20 Vcm−1
(b) may be equal to 20 Vcm−1
(c) may be greater than 20 Vcm−1
(d) may be less than 20 Vcm−1
A 10-cm long rod carries a charge of +50 μC distributed uniformly along its length. Find the magnitude of the electric field at a point 10 cm from both ends of the rod.
Consider a uniformly charged ring of radius R. Find the point on the axis where the electric field is maximum.
A particle of mass m and charge q is thrown at a speed u against a uniform electric field E. How much distance will it travel before coming to momentary rest ?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. Find the electric force and the force of gravity acting on this particle. Can one of these forces be neglected in comparison with the other for approximate analysis?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. How much is the work done by the electric force on the particle during this period?
A block of mass m with a charge q is placed on a smooth horizontal table and is connected to a wall through an unstressed spring of spring constant k, as shown in the figure. A horizontal electric field E, parallel to the spring, is switched on. Find the amplitude of the resulting SHM of the block. 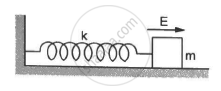
The electric potential existing in space is \[\hspace{0.167em} V(x, y, z) = A(xy + yz + zx) .\] (a) Write the dimensional formula of A. (b) Find the expression for the electric field. (c) If A is 10 SI units, find the magnitude of the electric field at (1 m, 1 m, 1 m).
The kinetic energy of a charged particle decreases by 10 J as it moves from a point at potential 100 V to a point at potential 200 V. Find the charge on the particle.
Find the magnitude of the electric field at the point P in the configuration shown in the figure for d >> a.
The surface charge density of a thin charged disc of radius R is σ. The value of the electric field at the center of the disc is `sigma/(2∈_0)`. With respect to the field at the center, the electric field along the axis at a distance R from the center of the disc ______.
Consider a region inside which, there are various types of charges but the total charge is zero. At points outside the region ______.
The Electric field at a point is ______.
- always continuous.
- continuous if there is no charge at that point.
- discontinuous only if there is a negative charge at that point.
- discontinuous if there is a charge at that point.
