Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A point charge q is rotated along a circle in an electric field generated by another point charge Q. The work done by the electric field on the rotating charge in one complete revolution is
पर्याय
zero
positive
negative
zero if the charge Q is at the centre, otherwise non-zero
उत्तर
zero
The electrostatic field is conservative and the work done by the field is a state function, i.e. it only depends on the initial and final positions of the charge but not on the path followed by it. In completing one revolution, the charge has the same initial and final positions. Therefore, the work done by the field on rotating the charge in one complete revolution is zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An infinite line charge produces a field of 9 × 104 N/C at a distance of 2 cm. Calculate the linear charge density.
When the separation between two charges is increased, the electric potential energy of the charges
The electric field at the origin is along the positive x-axis. A small circle is drawn with the centre at the origin, cutting the axes at points A, B, C and D with coordinates (a, 0), (0, a), (−a, 0), (0, −a), respectively. Out of the points on the periphery of the circle, the potential is minimum at
If a body is charged by rubbing it, its weight
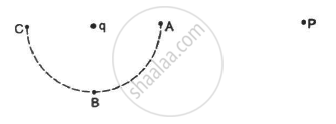
Consider the situation in the figure. The work done in taking a point charge from P to Ais WA, from P to B is WB and from P to C is WC.
The electric field in a region is directed outward and is proportional to the distance rfrom the origin. Taking the electric potential at the origin to be zero,
A particle of mass m and charge q is thrown at a speed u against a uniform electric field E. How much distance will it travel before coming to momentary rest ?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. What will be the speed of the particle after travelling this distance?
12 J of work has to be done against an existing electric field to take a charge of 0.01 C from A to B. How much is the potential difference VB − VA?
Find the magnitude of the electric field at the point P in the configuration shown in the figure for d >> a.
Which of the following methods can be used to charge a metal sphere positively without touching it? Select the most appropriate.
The surface charge density of a thin charged disc of radius R is σ. The value of the electric field at the center of the disc is `sigma/(2∈_0)`. With respect to the field at the center, the electric field along the axis at a distance R from the center of the disc ______.
In general, metallic ropes are suspended on the carriers taking inflammable materials. The reason is ______.
The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 100 W bulb at 3 m distance is E. The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 50 W bulb at the same distance is:
The Electric field at a point is ______.
- always continuous.
- continuous if there is no charge at that point.
- discontinuous only if there is a negative charge at that point.
- discontinuous if there is a charge at that point.
