Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In some old texts it is mentioned that 4π lines of force originate from each unit positive charge. Comment on the statement in view of the fact that 4π is not an integer.
उत्तर
4π is the total solid angle. "4π lines of force" is just a way of stating that the field lines extend uniformly in all directions away from the charge.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An infinite line charge produces a field of 9 × 104 N/C at a distance of 2 cm. Calculate the linear charge density.
Show that if we connect the smaller and the outer sphere by a wire, the charge q on the former will always flow to the latter, independent of how large the charge Q is.
Consider a system of n charges q1, q2, ... qn with position vectors `vecr_1,vecr_2,vecr_3,...... vecr_n`relative to some origin 'O'. Deduce the expression for the net electric field`vec E` at a point P with position vector `vecr_p,`due to this system of charges.
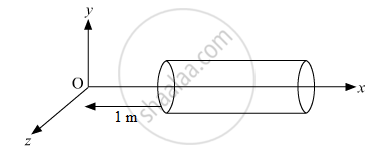
A hollow cylindrical box of length 1 m and area of cross-section 25 cm2 is placed in a three dimensional coordinate system as shown in the figure. The electric field in the region is given by `vecE = 50xhati` where E is NC−1 and x is in metres. Find
(i) Net flux through the cylinder.
(ii) Charge enclosed by the cylinder.
If a body is charged by rubbing it, its weight
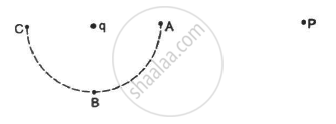
Consider the situation in the figure. The work done in taking a point charge from P to Ais WA, from P to B is WB and from P to C is WC.
A 10-cm long rod carries a charge of +50 μC distributed uniformly along its length. Find the magnitude of the electric field at a point 10 cm from both ends of the rod.
A particle of mass m and charge q is thrown at a speed u against a uniform electric field E. How much distance will it travel before coming to momentary rest ?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. What will be the speed of the particle after travelling this distance?
An electric field of 20 NC−1 exists along the x-axis in space. Calculate the potential difference VB − VA where the points A and B are
(a) A = (0, 0); B = (4 m, 2m)
(b) A = (4 m, 2 m); B = (6 m, 5 m)
(c) A = (0, 0); B = (6 m, 5 m)
Do you find any relation between the answers of parts (a), (b) and (c)?
Consider the situation of the previous problem. A charge of −2.0 × 10−4 C is moved from point A to point B. Find the change in electrical potential energy UB − UA for the cases (a), (b) and (c).
An electric field \[\vec{E} = ( \vec{i} 20 + \vec{j} 30) {NC}^{- 1}\] exists in space. If the potential at the origin is taken to be zero, find the potential at (2 m, 2 m).
The electric potential existing in space is \[\hspace{0.167em} V(x, y, z) = A(xy + yz + zx) .\] (a) Write the dimensional formula of A. (b) Find the expression for the electric field. (c) If A is 10 SI units, find the magnitude of the electric field at (1 m, 1 m, 1 m).
The kinetic energy of a charged particle decreases by 10 J as it moves from a point at potential 100 V to a point at potential 200 V. Find the charge on the particle.
Which of the following methods can be used to charge a metal sphere positively without touching it? Select the most appropriate.
When 1014 electrons are removed from a neutral metal sphere, the charge on the sphere becomes ______.
The Electric field at a point is ______.
- always continuous.
- continuous if there is no charge at that point.
- discontinuous only if there is a negative charge at that point.
- discontinuous if there is a charge at that point.
