Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of a suitable example and an equation, explain the term pair production.
उत्तर
Pair Production:
When a photon passes near a massive particle like an atomic nucleus, the photon disappears by creating an electron-positron pair. This process is called pair production. The energy of the photon should be equal to the sum of energy of electron and energy position. So a photon must have an energy of at least `2m_oc^2` to create an electron-positron pair. Where `m_o` is the rest mass of an electron.
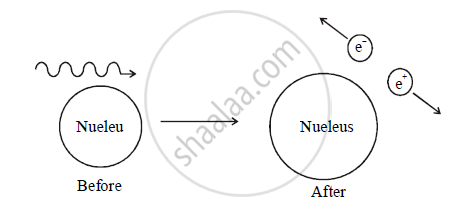
To conserve momentum, the nucleus recoils with very small velocity. Pair production is also known as the materialization of radiant energy.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the study of Geiger-Marsdon experiment on scattering of α particles by a thin foil of gold, draw the trajectory of α-particles in the coulomb field of target nucleus. Explain briefly how one gets the information on the size of the nucleus from this study.
From the relation R = R0 A1/3, where R0 is constant and A is the mass number of the nucleus, show that nuclear matter density is independent of A
The three stable isotopes of neon: `""_10^20"Ne"`, `""_10^21"Ne"` and `""_10^22"Ne"` have respective abundances of 90.51%, 0.27% and 9.22%. The atomic masses of the three isotopes are 19.99 u, 20.99 u and 21.99 u, respectively. Obtain the average atomic mass of neon.
Two nuclei have mass numbers in the ratio 1: 2. What is the ratio of their nuclear densities?
If neutrons exert only attractive force, why don't we have a nucleus containing neutrons alone?
A nucleus of mass number A has a radius R such that ______.
The mass number of a nucleus is equal to the number of:-
Are the nucleons fundamental particles, or do they consist of still smaller parts? One way to find out is to probe a nucleon just as Rutherford probed an atom. What should be the kinetic energy of an electron for it to be able to probe a nucleon? Assume the diameter of a nucleon to be approximately 10–15 m.
A nuclide 1 is said to be the mirror isobar of nuclide 2 if Z1 = N2 and Z2 = N1. (a) What nuclide is a mirror isobar of 1123 Na? (b) Which nuclide out of the two mirror isobars have greater binding energy and why?
James Chadwick, in 1932 studied the emission of neutral radiations when Beryllium nuclei were bombarded with alpha particles. He concluded that emitted radiations were neutrons and not photons. Explain.
Mass numbers of two nuclei are in the ratio of 4 : 3. Their nuclear densities will be in the ratio of ______.
