Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of a suitable example and an equation, explain the term pair production.
उत्तर
Pair Production:
When a photon passes near a massive particle like an atomic nucleus, the photon disappears by creating an electron-positron pair. This process is called pair production. The energy of the photon should be equal to the sum of energy of electron and energy position. So a photon must have an energy of at least
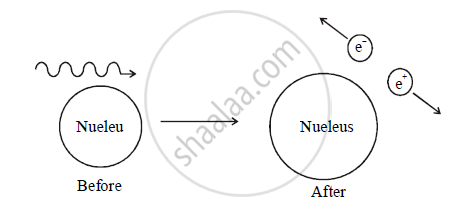
To conserve momentum, the nucleus recoils with very small velocity. Pair production is also known as the materialization of radiant energy.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the Q-value and the kinetic energy of the emitted α-particle in the α-decay of
Given
Name a material which is used in making control rods in a nuclear reactor.
Show that the density of nucleus over a wide range of nuclei is constant-independent of mass number A.
All nuclides with same mass number A are called ______.
The mass number of a nucleus is equal to the number of:-
Deuteron is a bound state of a neutron and a proton with a binding energy B = 2.2 MeV. A γ-ray of energy E is aimed at a deuteron nucleus to try to break it into a (neutron + proton) such that the n and p move in the direction of the incident γ-ray. If E = B, show that this cannot happen. Hence calculate how much bigger than B must E be for such a process to happen.
Before the neutrino hypothesis, the beta decay process was throught to be the transition,
Two nuclei have different mass numbers A1 and A2. Are these nuclei necessarily the isotopes of the same element? Explain.
James Chadwick, in 1932 studied the emission of neutral radiations when Beryllium nuclei were bombarded with alpha particles. He concluded that emitted radiations were neutrons and not photons. Explain.
What is 'Pair production'?
