Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write a commercial method for preparation of glucose.
How is glucose prepared on a commercial scale?
उत्तर
Commercial method for preparation of glucose: Commercially glucose is obtained by hydrolysis of starch by boiling it with dilute sulphuric acid at 393K under 2 to 3 atm pressure.
\[\ce{\underset{\text{Starch}}{(C6H10O5)}_{{n}} + {n}H2O ->[H+][393K, 2-3 atm] \underset{\text{Glucose}}{{n}C6H12O6}}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give scientific reasons:
Hydrolysis of sucrose is called inversion.
Write chemical reaction for following conversions
glucose into glucoxime
Define carbohydrates.
Draw the structure of the pyran.
Identify the given structure 'P' and 'Q'.
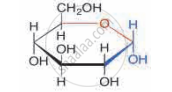
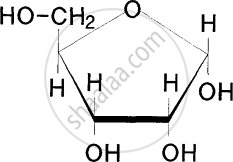
Identify the sugar having the molecular formula C6H1206.
Identify a non-reducing carbohydrate from the following.
Raffinose, sucrose and stachyose are respectively ____________.
Prolonged heating of glucose with hot HI results in the formation of ____________.
All these carbohydrates contain \[\ce{1 -> 4β}\] glycosidic linkage, EXCEPT ____________.
The general formula for polysaccharide is ____________.
Stachyose is ____________.
Which among the following statements is true for amylose?
What is the number of hydroxyl groups present in lactic acid?
Identify the number of secondary carbon atoms in glucose.
The correct corresponding order of names of four aldoses with configuration given below Respectively is:
Complete hydrolysis of cellulose gives ____________.
Classify the following into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
Sucrose
Write the structure of α-D (+) glucopyranose.
Corn is immersed in boiling water. It is then cooled, and the solution becomes sweet. It is due to ______.
Starch and cellulose are compounds made up of many units of ______.
The glycosidic linkage present in maltose is ______.
Describe the action of the following reagent on glucose:
Bromine water
Describe the action of the following reagent on glucose:
dil. Nitric acid.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
Why are carbohydrates generally optically active?
Write the Zwitter ion structure of alanine.
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
