Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write a note on bleeder’s disease and its inheritance with a suitable chart.
उत्तर
Haemophilia (Bleeder’s disease):
- Haemophilia is an X-linked recessive disorder in which blood fails to clot or coagulates very slowly.
- The genes for normal clotting are dominant over the recessive genes for haemophilia.
- The person having a recessive gene for haemophilia is deficient in clotting factors (VIII or IX) in blood.
- Even minor injuries cause continuous bleeding, hence haemophilia is also called bleeder’s disease.
- The recessive gene for haemophilia is located in a non-homologous region of the X chromosome.
- As there is no corresponding allele on the Y chromosome to suppress its expression, so men suffer from this disease.
- Women suffer only when both X chromosomes have recessive genes (alleles).
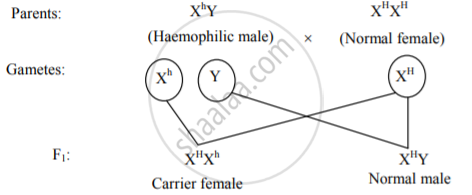
- If a haemophilic male (Xh Y) marries a female with the normal clotting of blood (XHXH), then all the offspring will show normal clotting of blood. The sons will have normal clotting of blood, but daughters will be carriers for the disease. The carriers have normal clotting of blood.
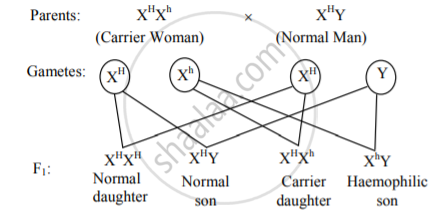
- When a carrier woman (XHXh ) marries a normal man (XHY), then all the daughters will have normal clotting of blood but half of them will be carriers for the disease. Half the sons will be haemophilic while the remaining will have normal clotting of blood.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain incomplete dominance with suitable example
If two individuals with blood group 'AB' marry and have sufficiently large number of children, these children could be classified as 'A' blood group : 'AB' blood group: 'B' blood group in 1 : 2 : 1 ratio. Modem technique of protein electrophoresis reveals presence of both 'A' and 'B' type proteins in 'AB' blood group individuals. This is an example of ______.
______ is an example of pleiotropy.
____________ is the genotypic and phenotypic ratio in incomplete dominance.
______ represents the genotype of a carrier carrying a gene for sickle-cell anaemia.
Which of the parents with the following blood groups CANNOT have a child with blood group A?
Which idea is depicted by a cross in which the F1 generation resembles both the parents?
ABO blood group system can be explained by ______.
Give a cross for incomplete dominance using a suitable example.
Fill in the blanks:
| Column 'A' (Gene interactions) |
Column 'B' (Example) |
|
| (1) | Co-dominance | ______ |
| (2) | Incomplete dominance | ______ |
| (3) | Multiple allelism | ______ |
| (4) | Pleiotropy | ______ |
| (5) | Polygenes | ______ |
| (6) | Autosomal dominance | ______ |
