Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write a note on bleeder’s disease and its inheritance with a suitable chart.
उत्तर
Haemophilia (Bleeder’s disease):
- Haemophilia is an X-linked recessive disorder in which blood fails to clot or coagulates very slowly.
- The genes for normal clotting are dominant over the recessive genes for haemophilia.
- The person having a recessive gene for haemophilia is deficient in clotting factors (VIII or IX) in blood.
- Even minor injuries cause continuous bleeding, hence haemophilia is also called bleeder’s disease.
- The recessive gene for haemophilia is located in a non-homologous region of the X chromosome.
- As there is no corresponding allele on the Y chromosome to suppress its expression, so men suffer from this disease.
- Women suffer only when both X chromosomes have recessive genes (alleles).
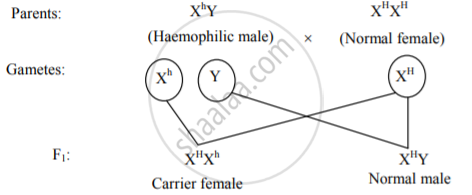
- If a haemophilic male (Xh Y) marries a female with the normal clotting of blood (XHXH), then all the offspring will show normal clotting of blood. The sons will have normal clotting of blood, but daughters will be carriers for the disease. The carriers have normal clotting of blood.
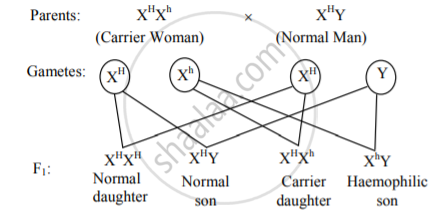
- When a carrier woman (XHXh ) marries a normal man (XHY), then all the daughters will have normal clotting of blood but half of them will be carriers for the disease. Half the sons will be haemophilic while the remaining will have normal clotting of blood.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why the ratio in pleiotropy is 2 : 1? Explain it with an example.
Explain the inheritance pattern of colour blindness with a suitable chart.
Explain intragenic and intergenic interaction with the help of example.
In ____________, one could get same genotypic and phenotypic ratio.
____________ is the genotypic and phenotypic ratio in incomplete dominance.
______ represents the genotype of a carrier carrying a gene for sickle-cell anaemia.
A gene which causes death of its bearer is ______.
In which of the following, are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios are same?
______ occurs when heterozygotes express both homozygous phenotypes equally.
Give a cross of co-dominance using a suitable example.
