Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write a short note on hyperconjucation.
उत्तर
The delocalisation of electrons of a bond is called as hyperconjugation. It is a special stabilising effect that results due to the interaction of electrons of a σ -bond (usually C – H or C – C) with the adjacent, empty non-bonding p-orbital or an anti¬bonding σ* or π*-orbitals resulting in an extended molecular orbital. Unlike the electromeric effect, hyper conjugation is a permanent effect.
It requires an α-CH group or a lone pair on atom-like N, O adjacent to a π bond (sp2 hybrid carbon). It occurs by the overlapping of the σ-bonding orbital or the orbital containing a lone pair with the adjacent π-orbital or p-orbital.
Example:
In propene, the σ -electrons of C-H bond of methyl group can be delocalised into the π -orbital of doubly bonded carbonas represented below.
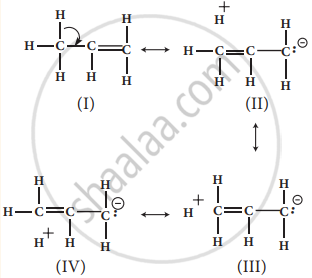
No bond resonance structures shown by propene are due to hyperconjugation
In the above structure, the sigma bond is involved in resonance and breaks in order to supply electrons for delocalization giving rise to 3 new canonical forms. In the contributing canonical structures: (Il), (III) & (IV) of propene, there is no bond between an α-carbon and one of the hydrogen atoms. Hence the hyperconjugation is also known as “no bond resonance” or “Baker Nathan effect”. The structures (II), (III) & (IV) are polar in nature.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the hybridisation state of benzyl carbonium ion?
Which of the following species is not electrophilic in nature?
Hyper Conjugation is also known as
Which of the following species does not exert a resonance effect?
- I effect is shown by ______.
Heterolytic fission of C–C bond results in the formation of ______.
Which of the following represent a set of nucleophiles?
Which of the following species does not acts as a nucleophile?
Write a short note on resonance.
What is electrophiles? Give a suitable example.
