Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write down the properties of electromagnetic waves.
उत्तर
- Electromagnetic waves are produced by any accelerated charge.
- Electromagnetic waves do not require any medium for propagation. So electromagnetic wave is a non-mechanical wave.
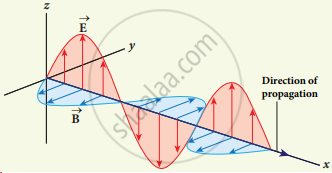
- Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature. This means that the oscillating electric field vector, oscillating magnetic field vector and propagation vector (gives direction of propagation) are mutually perpendicular to each other.
- Electromagnetic waves travel with speed which is equal to the speed of light in vacuum or free space, c = `1/sqrt(epsilon_0mu_0) 3 xx 10^8 "ms"^-1`
- The speed of electromagnetic wave is less than speed in free space or vacuum, that is, v < c. In a medium of refractive index,
`mu_0 = "c"/"v" = (1/sqrt(epsilon_0mu_0))/(1/sqrt(epsilonmu))`
`=> mu = sqrt(epsilon_"r"mu_"r")`, - Electromagnetic waves are not deflected by electric field or magnetic field.
- Electromagnetic waves can show interference, diffraction and can also be polarized.
- The energy density (energy per unit volume) associated with an electromagnetic wave propagating in vacuum or free space is
u = `1/2 epsilon_0 "E"^2 + 1/(2mu_0) "B"epsilon^2`
Where, `1/2`ε0 E2 = uE is the energy density in an electric field and `1/(2mu_0)` Bε2 = uB is the energy density in a magnetic field.
Since, E = Bc ⇒ uB = uE.
The energy density of the electromagnetic wave is = ε E2 = -B2 - The average energy density for electromagnetic wave, ⟨u⟩ = `1/2`ε0 E2 = `1/2 1/mu_0` Bε2
- The energy crossing per unit area per unit time and perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave is called the intensity.
Intensity, I = ⟨u⟩c - Like other waves, electromagnetic waves also carry energy and momentum. For the electromagnetic wave of energy U propagating with speed c has linear momentum which is given by = `"Energy"/"speed" = "U"/"c"`. The force exerted by an electromagnetic wave on unit area speed of a surface is called radiation pressure.
- If the electromagnetic wave incident on a material surface is completely absorbed, then the energy delivered is U and momentum imparted on the surface is p = `"U"/"c"`.
- If the incident electromagnetic wave of energy U is totally reflected from the surface, then the momentum delivered to the surface is ∆p = `"U"/"c" - (- "U"/"c") = 2 "U"/"c"`.
- The rate of flow of energy crossing a unit area is known as pointing vector for electromagnetic waves, which is `vec"S" = 1/mu_0 (vec"E" xx vec"B") =`c2ε0 `(vec"E" xx vec"B")`. The unit for the pointing vector is W m-2. The pointing vector at any point gives the direction of energy transport from that point.
- Electromagnetic waves carries not only energy and momentum but also angular momentum.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A plane electromagnetic wave is travelling through a medium along the +ve z-direction. Depict the electromagnetic wave showing the directions of the oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
What are the directions of electric and magnetic field vectors relative to each other and relative to the direction of propagation of electromagnetic waves?
How does a charge q oscillating at certain frequency produce electromagnetic waves?
Sketch a schematic diagram depicting electric and magnetic fields for an electromagnetic wave propagating along the Z-direction.
Write notes on Ampere-Maxwell law.
In plane electromagnetic wave propagation velocity v, wavelength λ and frequency ν are related by ______.
Light with an energy flux of 20 W/cm2 falls on a non-reflecting surface at normal incidence. If the surface has an area of 30 cm2 the total momentum delivered (for complete absorption) during 30 minutes is ______.
An electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z direction: `E = ( E_1hati + E_2hatj ) cos (kz - ωt)`. Choose the correct options from the following:
- The associated magnetic field is given as `B = 1/c(E_1hati - E_2hatj) cos (kz - ωt)`.
- The associated magnetic field is given as `B = 1/c(E_1hati - E_2hatj) sin (kz - ωt)`.
- The given electromagnetic field is circularly polarised.
- The given electromagnetic wave is plane polarised.
The source of electromagnetic waves can be a charge ______.
- moving with a constant velocity.
- moving in a circular orbit.
- at rest.
- falling in an electric field.
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in free space along the x-direction. The electric field component of the wave at a particular point of space and time is E = 6 Vm-1 along the y-direction. Its corresponding magnetic field component, B would be ______.
A plane electromagnetic wave with frequency of 30 MHz travels in free space. At particular point in space and time, electric field is 6 V/m. The magnetic field at this point will be x × 10-8 T. The value of x is ______.
