Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write scientific reason.
The value of acceleration g is greater at the pole than at the equator.
उत्तर
- The shape of the earth is not perfectly spherical. It is slightly flattened at the poles and bulged at the equator.
- As a result, the radius of the earth at the poles is less than that at the equator.
- But, acceleration due to gravity (g) on earth’s surface is given as, g = `"GM"/"R"^2`, therefore acceleration due to gravity increases with the decrease in radius of earth and vice versa.
- Hence, the value of acceleration due to gravity (g) is greater at the pole than at the equator.
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the value of gravitational constant G (i) on the earth, and (ii) on the moon ?
State whether the following statement is true or false :
The value of G on the moon is about one-sixth `(1/6)`of the value of G on the earth.
If the value of g suddenly becomes twice its value, it will become two times more difficult to pull a heavy object along the floor. Why?
The radius of planet A is half the radius of planet B. If the mass of A is MA, what must be the mass of B so that the value of g on B is half that of its value on A?
The value of g is highest at the equator.
The value of G varies from place to place.
As we go above the earth's surface, value of g increases.
The mass of the moon is `1/81` of the mass of the earth. Its diameter is `1/3.7` of that of the earth. If acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth is 9.8 m/s2, then the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon.
The mass of a body on the surface of the earth is 10 kg. The mass of the same body on the surface on the moon is `"g"_"m" = 1/6 "g"_"e"`, where gm, ge acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon and the earth respectively.
The depth 'd' below the surface of the earth at which acceleration due to gravity becomes `(g/n)` is ______.
R = radius of the earth, 'g' = acceleration due to gravity, n = integer
The acceleration due to gravity on moon is `(1/6)^"th"` times the acceleration due to gravity on earth. If the ratio of the density of earth 'ρe' to the density of moon 'ρm' is `5/3`, then the radius of moon 'Rm' in terms of the radius of earth 'Re' is ______.
The radius of the orbit of a geostationary satellite is (mean radius of the earth R, angular velocity about an axis in ω and acceleration due to gravity on earth's surface is (g) ______.
In the relation F = `"G M" "m"//"d"^2`, the quantity G
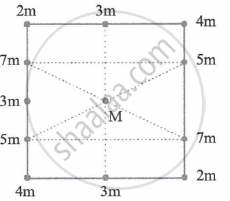
A central particle M is surrounded by a square array of other particles, separated by either distanced or distance d/2 along the perimeter o the square. The magnitude of the gravitational force on the central particle due to the other particles is ______.
A mass attached to one end of a string crosses top-most point on a vertical circle with critical speed. Its centripetal acceleration when string becomes horizontal will be ______. (g = gravitational acceleration)
The acceleration due to gravity on the earth of radius Re is ge, and that on moon of radius Rm, is gm. The ratio of the masses of the earth and moon is given by ______.
