Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
3: Periodic Classification Of Elements
4: Hydrogen
5: Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals
6: Gaseous State
7: Thermodynamics
8: Physical and Chemical Equilibrium
9: Solutions
10: Chemical bonding
▶ 11: Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
12: Basic concept of organic reactions
13: Hydrocarbons
14: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
15: Environmental Chemistry
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 11 - Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 11 - Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 11: Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 11 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board 11 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Evaluation [Pages 153 - 158]
Choose the best answer
Select the molecule which has only one π bond.
CH3 – CH = CH – CH3
CH3 – CH = CH – CHO
CH3 – CH = CH – COOH
All of these
In the hydrocarbon
![]() the state of hybridisation of carbon 1,2,3,4 and 7 are in the following sequence.
the state of hybridisation of carbon 1,2,3,4 and 7 are in the following sequence.
sp, sp, sp3, sp2, sp3
sp2, sp, sp3, sp2, sp3
sp, sp, sp2, sp, sp3
none of these
The general formula for alkadiene is ______.
CnH2n
`"C"_"n""H"_(2"n" – 1)`
`"C"_"n""H"_(2"n" – 2)`
`"C"_"n""H"_("n" – 2)`
Structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is 5, 6 – dimethylhept - 2 - ene is
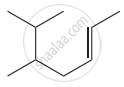
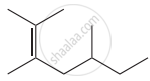
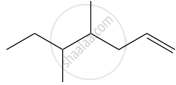
None of these
The IUPAC name of the compound is
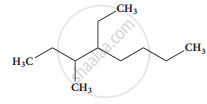
2,3 - Diemethylheptane
3- Methyl -4- ethyloctane
5-ethyl -6-methyloctane
4-Ethyl -3 - methyloctane
Which one of the following names does not fit a real name?
3 - Methyl - 3 - hexanone
4 - Methyl - 3 - hexanone
3 - Methyl - 3 hexanol
2 - Methyl cyclo hexanone
The IUPAC name of the compound \[\ce{CH3 - CH = CH - C ≡ CH}\] is ______.
Pent – 4- yn – 2 – ene
Pent – 3- en – 1- yne
Pent – 2 – en – 4 – yne
Pent – 1 yn – 3 – ene
IUPAC name of \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{....}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{C4H9}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\\ce{CH3 - C - C - CH3}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\\phantom{.....}\ce{C2H5}\phantom{.}\ce{CH3}\phantom{...}\end{array}\] is
3, 4, 4 – Trimethylheptane
2 – Ethyl – 3, 3, – dimethyl heptane
3, 4, 4 – Trimethyloctane
2 – Butyl – 2 – methyl – 3 ethyl – butane
The IUPAC name of \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.}\ce{CH3}\\|\phantom{..}\\
\ce{H3C - C - CH = C(CH3)2}\\
|\phantom{..}\\\phantom{..}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\] is
2,4,4 – Trimethylpent – 2 – ene
2,4,4 – Trimethylpent – 3 – ene
2,2,4 – Trimethylpent – 3 – ene
2,2,4 – Trirnethylpent – 2 – ene
The IUPAC name of the compound\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3-CH=C-CH2-CH3}\\
|\phantom{..}\\\phantom{...............}\ce{CH2 - CH2 - CH3}\end{array}\] is
3 – Ethyl – 2 – hexene
3 – Propyl – 3 – hexene
4 – Ethyl – 4 – hexene
3 – Propyl – 2 – hexene
The IUPAC name of the compound \[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3 - CH - COOH}\\
|\phantom{.....}\\\ce{OH}\phantom{...}
\end{array}\] is
2 – Hydroxypropionic acid
2 – Hydroxy Propanoic acid
Propan – 2 – ol – 1 – oic acid
1 – Carboxyethanol
The IUPAC name of \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................}\\
\backslash\phantom{....................}\\
\ce{CH - CH - COOH}\\/\phantom{.......}|\phantom{.............}\\
\ce{Br}\phantom{.......}\ce{CH3}\phantom{...........}\\\end{array}\] is
2 – Bromo – 3- methyl butanoic acid
2 – methyl – 3 bromo butanoic acid
2 – methyl – 3 bromo butanoic acid
3 – Bromo – 2, 3 – dimethyl propanoic acid
The structure of isobutyl group in an organic compound is
CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2
\[\begin{array}{cc}\phantom{..........}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{.......}|\\\ce{CH3 - C}\\
\phantom{.......}|\\\phantom{.........}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3 - CH - CH2 -}\\
|\phantom{.....}\\\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\end{array}\]\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3 - CH - CH2 - CH3}\\
|\phantom{.........}\end{array}\]
The number of stereoisomers of 1, 2 – dihydroxy cyclopentane
1
2
3
4
Which of the following is optically active?
3 – Chloropentane
2- Chloro propane
Meso – tartaric acid
Glucose
The isomer of ethanol is ______.
acetaldehyde
dimethyl ether
acetone
methyl carbinol
How many cyclic and acyclic isomers are possible for the molecular formula C3H6O?
4
5
9
10
Which one of the following shows functional isomerism?
ethylene
Propane
ethanol
CH2Cl2
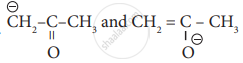 are
are
resonating structure
tautomers
Optical isomers
Conformers
Nitrogen detection in an organic compound is carried out by Lassaigne’s test. The blue colour formed is due to the formation of
Fe3[Fe(CN)6]2
Fe4 [Fe(CN)6]3
Fe4[Fe(CN)6]2
Fe3[Fe(CN)6]3
Lassaigne’s test for the detection of nitrogen fails in ______.
\[\ce{H2N - CO - NH*NH2*HCl}\]
\[\ce{NH2 - NH2*HCl}\]
\[\ce{C6H5 - NH - NH2*HCl}\]
\[\ce{C6H5CONH2}\]
Connect pair of compounds which give blue colouration/precipitate and white precipitate respectively, when their Lassaigne’s test is separately done.
NH2 NH2 HCl and ClCH2 – CHO
NH2 CS NH2 and CH3 – CH2Cl
NH2 CH2 COOH and NH2 CONH2
C6H5NH2 and ClCH2 – CHO
Sodium nitropruside reacts with sulphide ion to give a purple colour due to the formation of ______.
[Fe (CN)5 NO]3-
[Fe (NO)5 CN]+
[Fe (CN)5 NOS]4-
[Fe (CN)5 NOS]3-
An organic Compound weighing 0.15g gave on carius estimation, 0.12g of silver bromide. The percentage of bromine in the Compound will be close to ______.
46%
34%
3.4%
4.6%
A sample of 0.5 g of an organic compound was treated according to Kjeldahl’s method. The ammonia evolved was absorbed in 50mL of 0.5 M H2SO4 The remaining acid after neutralization by ammonia consumed 80 mL of 0.5 M NaOH. The percentage of nitrogen in the organic compound is.
14%
28%
42%
56%
In an organic compound, phosphorus is estimated as ______.
Mg2P2O7
Mg3(PO4)2
H3PO4
P2O 5
Ortho and para – nitro phenol can be separated by ______.
azeotropic distillation
destructive distillation
steam distillation
cannot be separated
The purity of an organic compound is determined by ______.
Chromatography
Crystallisation
melting or boiling point
both Chromatography and melting or boiling point
A liquid which decomposes at its boiling point can be purified by ______.
distillation at atmospheric pressure
distillation under reduced pressure
fractional distillation
steam distillation
Assertion: \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH - C = CH - COOH}\\|\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{........}\ce{COOC2H5}\end{array}\]
Reason: The principal functional group gets lowest number followed by double bond (or) triple bond.
both the assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
both assertion and reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
assertion is true but reason is false.
both the assertion and reason are false
Write brief answer to the following questions.
Give the general characteristics of organic compounds.
Describe the classification of organic compounds based on their structure.
Write a note on homologous series.
Identify the functional group in the following compound.
Acetaldehyde
Identify the functional group in the following compound.
Oxalic acid
Identify the functional group in the following compound.
Di methyl ether
Identify the functional group in the following compound.
Methylamine
What is meant by a functional group?
Give the general formula for the following class of organic compound.
Aliphatic monohydric alcohol
Give the general formula for the following class of organic compound.
Aliphatic ketones
Give the general formula for the following class of organic compound.
Aliphatic amines
Write the molecular formula of the first six members of homologous series of nitro – alkanes.
Write the molecular formula and possible structural formula of the first four members of homologous series of carboxylic acids.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
\[\ce{(CH3)2 CH–CH2 –CH(CH3 )–CH(CH3)2}\]
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - CH3}\\
\phantom{...}|\phantom{......}|\phantom{.....}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{...}\ce{Br}\phantom{.}
\end{array}\]
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
\[\ce{CH3 - O - CH3}\]
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH - CHO}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\\phantom{.......}\ce{OH}
\end{array}\]
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
\[\ce{CH2 = CH - CH = CH2}\]
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3 - C ≡ C - CH - CH3}\\
\phantom{........}|\\\phantom{.........}\ce{Cl}
\end{array}\]
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
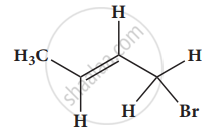
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
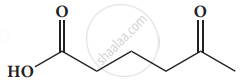
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
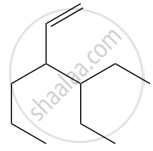
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
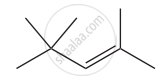
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
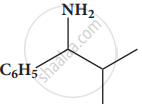
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
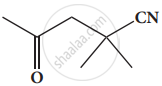
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.

Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
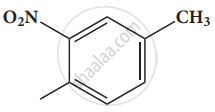
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
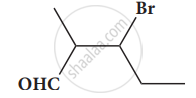
Give the structure for the following compound.
3 – ethyl – 2 methyl – 1 – pentene
Give the structure for the following compound.
1,3,5- Trimethyl cyclohex - 1 -ene
Give the structure for the following compound.
tertiary butyl iodide
Give the structure for the following compound.
3 - Chlorobutanal
Give the structure for the following compound.
3 - Chlorobutanol
Give the structure for the following compound.
2 - Chloro - 2- methyl propane
Give the structure for the following compound.
2,2-dimethyl-1-chloropropane
Give the structure for the following compound.
3 - methylbut -1- ene
Give the structure for the following compound.
Butan - 2, 2 - diol
Give the structure for the following compound.
Octane - 1,3- diene
Give the structure for the following compound.
1,3- Dimethylcyclohexane
Give the structure for the following compound.
3-Chlorobut - 1 - ene
Give the structure for the following compound.
3 - methylbutan - 2 - ol
Give the structure for the following compound.
acetaldehyde
Describe the reactions involved in the detection of nitrogen in an organic compound by Lassaigne method.
Give the principle involved in the estimation of halogen in an organic compound by Carius method.
Give a brief description of the principles of Fractional distillation.
Give a brief description of the principle of column Chromatography.
Explain paper chromatography.
Explain various types of constitutional isomerism (structural isomerism) in organic compounds.
Describe optical isomerism with a suitable example.
Describe optical isomerism with a suitable example.
Briefly explain geametrical isomerism in alkene by considering 2-butene as an example.
0.30 g of a substance gives 0.88 g of carbon dioxide and 0.54 g of water calculate the percentage of carbon and hydrogen in it.
The ammonia evolved form 0.20 g of an organic compound by Kjeldahl method neutralized 15 ml of N/20 sulphuric acid solution. Calculate the percentage of Nitrogen.
0.32 g of an organic compound, after heating with fuming nitric acid and barium nitrate crystals is a sealed tube game 0.466 g of barium sulphate. Determine the percentage of sulphur in the compound.
0.24g of an organic compound gave 0.287 g of silver chloride in the carius method. Calculate the percentage of chlorine in the compound.
In the estimation of nitrogen present in an organic compound by Dumas method 0.35 g yielded 20.7 mL of nitrogen at 15° C and 760 mm pressure. Calculate the percentage of nitrogen in the compound.
Solutions for 11: Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 11 - Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 11 - Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 11 - Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 11 (Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 11 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry are Introduction to Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry, Classification of Organic Compounds, Nomenclature of Organic Compounds, Structural Representation of Organic Compounds, Isomerism in Organic Compounds, Detection of Elements in Organic Compounds, Estimation of Elements, Introduction of Methods of Purification of Organic Compounds.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board solutions Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 11, Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
