Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
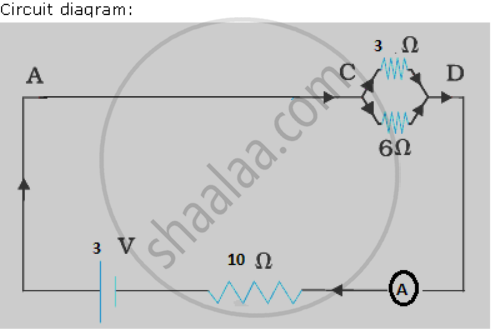
A battery o f e.m.f. 3 Vis connected in series with an ammeter, a 10 Ω coil of wire and with a parallel combination o f resistance of 3Ω and 6 Ω. Draw a circuit diagram for the above arrangement. What is the
(a) Resistance of the parallel combination?
(b) Reading on the ammeter?
( c) Potential difference across the 3Ω resistor?
( d) Current flowing through each resistor?
Solution
(a) Resistance of parallel combination:
`1/"R"_"parallel" = 1/3 + 1/6 = 3/6 = 1/2` Ω
`"R"_"parallel" = 2`Ω
(b) Total resistance of the circuit =
`"R"_"total" = 2 + 10= 12`Ω
Let I be the current through the ammeter, the:
I = `"V"/"R"_"total" = 3/12 = 1/4` = 0.25 A
(c) Potential drop across 10 0 resistor, V1 = I x 10= 0.25 x 10 = 2.5V
:. Potential drop across 3Ω resistor, V2 = e - V1 = 3 - 2.5 = 0.5V
(d) Current flowing through 10 Ω resistor= 0.25 A
Current flowing through 3 Ω resistor = `"V"_2/"R" = 0.5/3` = 0.17 A
Current flowing through 6 Ω resistor= 0.25 · 0.17 = 0.08 A
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An electric bulb of 300Ω draws a current of 0.4 A. Calculate the power of the bulb and the potential difference at its ends.
Explain the meaning of the term e.m.f. of a cell.
State the factors on which the e.m.f of a cell depends.
A cell of e.m.f. E and internal resistance r is used to send current I in an external resistance R. Write expressions for (i) the current drawn from the cell,
(ii) the terminal voltage V of the cell, and
(iii) the voltage drop across the internal resistance. How are E and V related?
A cell of e.m.f. 1.5 V and internal resistance 1.0 W is connected to two resistors of 4.0 W and 20.0 in series as shown in the figure: Calculate the:
(i) Current in the circuit.
(ii) Potential difference across the 4.0 ohm resistor.
(iii) Voltage drop when the current is flowing.
(iv) Potential difference across the cell.
The e.m.f of a cell is analogues to ______ of a pipe line.
Electrons in outer orbits are called free electrons.
Define the following:
Electromotive force (e.m.f.)
