Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A body starts from rest and acquires a velocity 10 m s-1 in 2 s. Find the acceleration.
Solution
Here, final velocity = 10 m/s
Initial velocity = 0 m/s
Time taken = 2s
Acceleration = (Final Velocity - Initial Velocity)/time
= (10/2) ms-2
= 5 ms-2
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When will you say a body is at non-uniform acceleration?
Give one example of a situation in which a body has a certain average speed but its average velocity is zero.
A bus running at a speed of 18 km/h is stopped in 2.5 seconds by applying brakes. Calculate the retardation produced.
Derive the formula : v = u + at, where the symbols have usual meanings.
A car is travelling along the road at 8 ms-1. It accelerates at 1 ms-2 for a distance of 18 m. How fast is it then travelling ?
Differentiate between uniform acceleration and variable acceleration.
A bicycle initially moving with a velocity 5.0 m s-1 accelerates for 5 s at a rate of 2 m s-2. What will be its final velocity?
When is the positive acceleration?
How can you find the following?
Acceleration from velocity – time graph.
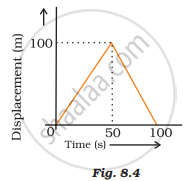
A girl walks along a straight path to drop a letter in the letterbox and comes back to her initial position. Her displacement–time graph is shown in Fig.8.4. Plot a velocity-time graph for the same.