Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A capacitor of capacitance 10 μF is connected to an oscillator with output voltage ε = (10 V) sin ωt. Find the peak currents in the circuit for ω = 10 s−1, 100 s−1, 500 s−1 and 1000 s−1.
Solution
Capacitance of the capacitor, C = 10 μF = 10 × 10−6 F = 10−5 F
Output voltage of the oscillator, ε = (10 V)sinωt
On comparing the output voltage of the oscillator with
` ε = ε_0 `, we get:
Peak voltage ε0 = 10 V
For a capacitive circuit,
Reactance, `X_e=1/(omegaC)`
Here, `omega` = angular frequency
C = capacitor of capacitance
Peak current, `I_0 = ε_0 /X_e`
(a) At ω = 10 s−1:
Peak current,
I0 = `ε_0/X_e`
= `ε_0/(1/omegaC)`
= `10/(1//10xx10^-5 )A`
= 1 × 10−3 A
(b) At ω = 100 s−1:
Peak current, I0 = `ε_0 /(1//omegaC)`
⇒` I_0 = 10/(1/100xx10^-5)`
⇒ `I_0 = 10/(1//100xx10^-5)`
⇒ `I_0 = 10/10^3 = 1xx10^-2 A`
= 0.01 A
(c) At ω = 500 s−1:
Peak current, I0 = `ε_0/(1//omegaC)`
`I_0 = epsilon_0/(1//omegaC)`
`⇒ I_0 = 10/(1//5xx10^-5)`
= `5xx10^-2 A =0.05 A`
(d) At ω = 1000 s−1:
Peak current, I0 = `epsilon_0/(1/omegaC)`
⇒ `I_0 = 10/(1//1000xx10^-5)`
⇒ `I_0 =10xx1000xx10^-5`
⇒ `I_0= 10^-1 A = 0.1 A`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A device X is connected across an ac source of voltage V = V0 sin ωt. The current through X is given as
`I = I_0 sin (omega t + pi/2 )`
1) Identify the device X and write the expression for its reactance.
2) Draw graphs showing the variation of voltage and current with time over one cycle of ac, for X.
3) How does the reactance of the device X vary with the frequency of the ac? Show this variation graphically.
4) Draw the phasor diagram for the device X.
The voltage and current in a series AC circuit are given by V = V0cos ωt and i = i0 sin ωt. What is the power dissipated in the circuit?
Two alternating currents are given by `i_1 = i_0 sin wt and i_2 = i_0 sin (wt + pi/3)` Will the rms values of the currents be equal or different?
An alternating current is given by i = i1 cos ωt + i2 sin ωt. The rms current is given by
A constant current of 2.8 A exists in a resistor. The rms current is
Find the time required for a 50 Hz alternating current to change its value from zero to the rms value.
The household supply of electricity is at 220 V (rms value) and 50 Hz. Find the peak voltage and the least possible time in which the voltage can change from the rms value to zero.
A coil of inductance 5.0 mH and negligible resistance is connected to the oscillator of the previous problem. Find the peak currents in the circuit for ω = 100 s−1, 500 s−1, 1000 s−1.
The peak voltage of an ac supply is 300 V. What is the rms voltage?
Phase diffn between voltage and current in a capacitor in A.C Circuit is.
In a transformer Np = 500, Ns = 5000. Input voltage is 20 volt and frequency is 50 HZ. Then in the output, we have,
When a voltage measuring device is connected to AC mains, the meter shows the steady input voltage of 220V. This means ______.
The output of a step-down transformer is measured to be 24 V when connected to a 12-watt light bulb. The value of the peak current is ______.
RMS value of an alternating current flowing in a circuit is 5A. Calculate its peak value.
In the Figure below, the current-voltage graphs for a conductor are given at two different temperatures, T1 and T2.
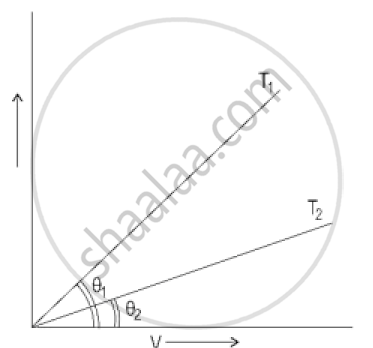
- At which temperature T1 or T2 is the resistance higher?
- Which temperature (T1 or T2) is higher?
