Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The output of a step-down transformer is measured to be 24 V when connected to a 12-watt light bulb. The value of the peak current is ______.
Options
`1/sqrt(2) A`
`sqrt(2) A`
2 A
`2sqrt(2) A`
Solution
The output of a step-down transformer is measured to be 24 V when connected to a 12-watt light bulb. The value of the peak current is `underline(1/sqrt(2) A)`.
Explanation:
It decreases voltage and increases current
|
VS < VP NS < NP ES < EP iS < iP RS < RP tS < tP kS < 1 |
 |
According to the problem output/secondary voltage VS = 24 V
Power associated with secondary PS = 12 W
`I_S = P_S/V_S = 12/24` = 0.5 A
Amplitude of the current in the secondary winding
`I _O = I_S sqrt(2)`
= `(0.5)(1.414) = 0.707 = 1/sqrt(2) A`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A device X is connected across an ac source of voltage V = V0 sin ωt. The current through X is given as
`I = I_0 sin (omega t + pi/2 )`
1) Identify the device X and write the expression for its reactance.
2) Draw graphs showing the variation of voltage and current with time over one cycle of ac, for X.
3) How does the reactance of the device X vary with the frequency of the ac? Show this variation graphically.
4) Draw the phasor diagram for the device X.
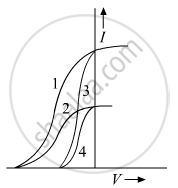
The given graph shows the variation of photo-electric current (I) versus applied voltage (V) for two difference photosensitive materials and for two different intensities of the incident radiations. Identify the pairs of curves that correspond to different materials but same intensity of incident radiation.
Can the peak voltage across the inductor be greater than the peak voltage of the source in an LCR circuit?
The dielectric strength of air is 3.0 × 106 V/m. A parallel-plate air-capacitor has area 20 cm2 and plate separation 0.10 mm. Find the maximum rms voltage of an AC source that can be safely connected to this capacitor.
A coil of inductance 5.0 mH and negligible resistance is connected to the oscillator of the previous problem. Find the peak currents in the circuit for ω = 100 s−1, 500 s−1, 1000 s−1.
In a series RC circuit with an AC source, R = 300 Ω, C = 25 μF, ε0 = 50 V and ν = 50/π Hz. Find the peak current and the average power dissipated in the circuit.
A small town with a demand of 800 kW of electric power at 220 V is situated 15 km away from an electric plant generating power at 440 V. The resistance of the two wire line carrying power is 0.5 Ω per km. The town gets power from the line through a 4000-220 V step-down transformer at a sub-station in the town.
(a) Estimate the line power loss in the form of heat.
(b) How much power must the plant supply, assuming there is negligible power loss due to leakage?
(c) Characterise the step up transformer at the plant.
Do the same with the replacement of the earlier transformer by a 40,000-220 V step-down transformer (Neglect, as before, leakage losses though this may not be a good assumption any longer because of the very high voltage transmission involved). Hence, explain why high voltage transmission is preferred?
The period of oscillation of a simple pendulum is T = `2π sqrt"L"/"g"`. The measured value of L is 20.0 cm known to have 1 mm accuracy and the time for 100 oscillations of the pendulum is found to be 90 s using a wristwatch of ls resolution. The accuracy in the determination of g is:
